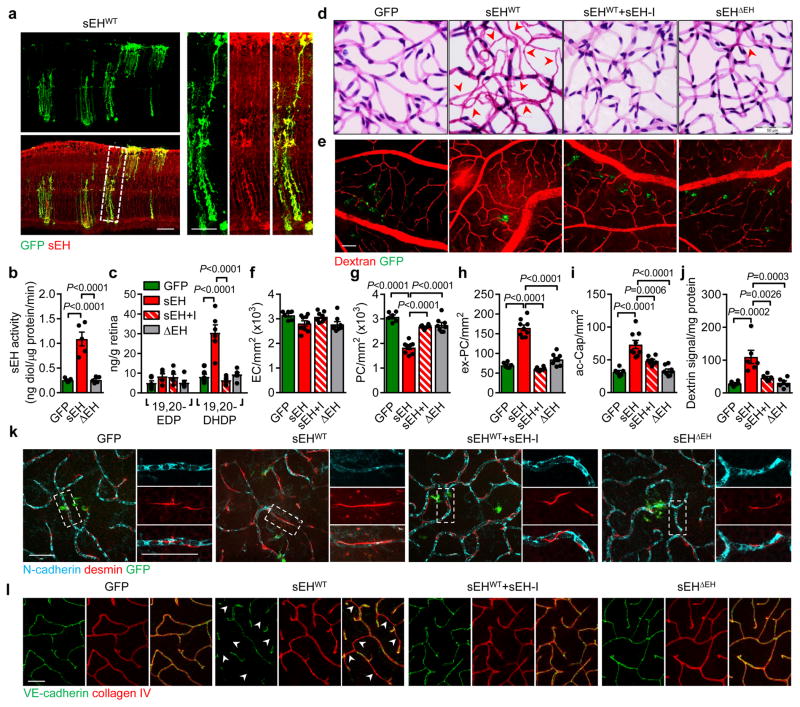
Fig. 4. sEH-induced retinopathy in non-diabetic mice.
(a) sEH (red) in wild-type mice retinas 7 days after intravitreal injection of GFP track adenoviral-sEH (sEHWT). (b) Retinal sEH activity 14 days after intravitreal injection of adenoviruses encoding GFP, sEHWT or the sEHΔEH mutant. (c) 19,20-EDP/DHDP levels in retinas 14 days after adenoviral injection to animals receiving vehicle or the sEH inhibitor (sEH-I). (d) Retinal digest preparations 14 days after adenovirus injection with or without sEH inhibitor (+I) treatment. Acellular capillaries are marked by arrowheads. (e) Vascular permeability (titrc-dextrin; red) 14 days after virus administration. (f–i) Quantitative retinal morphometry of images in d; i.e., endothelial cells (EC, f), pericytes (PC, g), extravascular pericytes (Ev-PC, h), and acellular capillaries (ac-Cap, i); n = 6 (GFP), 9 (sEHWT) or 8 (sEHWT+I, sEHΔEH) mice per group. (j) Quantification of leaked Titrc-dextrin. (k) N-cadherin (cyan) and desmin (red) in retinas treated with adenoviruses. Note the perivascular desmin positive protrusions that mark extravascular pericytes in sEHWT treated retinas. (l) VE-cadherin (green) and collagen IV (red) in retinas 14 days after adenovirus injection. Capillaries with abnormal VE-cadherin indicated with arrowheads. Scale bars 50μm. n = 5 (b), 6 (e, j–l) mice or 6 biologically independent samples per group (c). Data are mean ± s.e.m. P values determined by 1way ANOVA.