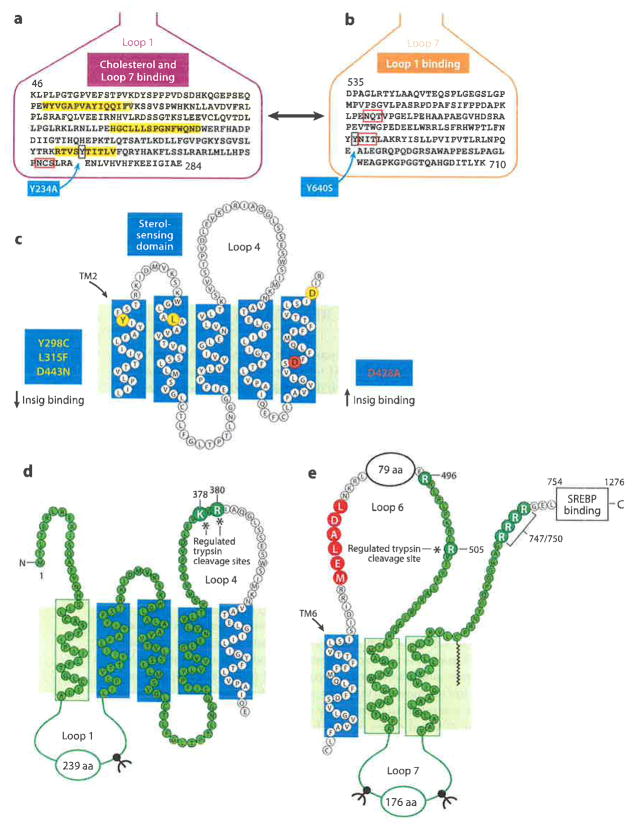
Figure 4.
A more detailed view of the domains of Scap. (a) This sequence of Loop 1 shows three short hydrophobic sequences (yellow), a single N-linked glycosylation site (red box), and tyrosine-234 (blue box). (b) This sequence of Loop 7 shows locations of two N-linked sites (red boxes) and tyrosine-640 (blue box). (c) The sterol-sensing domain (TMs 2–6) contains three residues (Y298, L315, D443) (yellow circles), each of which is required for binding Insigs, and one residue (D428) (red circle), which is required for dissociation from Insigs in the absence of cholesterol. (d) Basic residues in Loop 4 (K378 and R380) that are cleaved by trypsin only when membranes are depleted of cholesterol. This fragment is identified by probing SDS gels with anti-Loop 1 antibody (highlighted in green). (e) Arginine in Loop 6 (R505) that is cleaved by trypsin only in cholesterol-enriched membranes. This fragment is recognized by probing SDS gels with anti-Loop 7 antibody (highlighted in green). Abbreviations: SDS, sodium dodecyl sulfate; SREBP, sterol regulatory element-binding protein; TMs, transmembrane helices.