Figure 1. Comparison of CFZ and CFZ analog 568: structures, precipitation assay, and absorbance profiles.
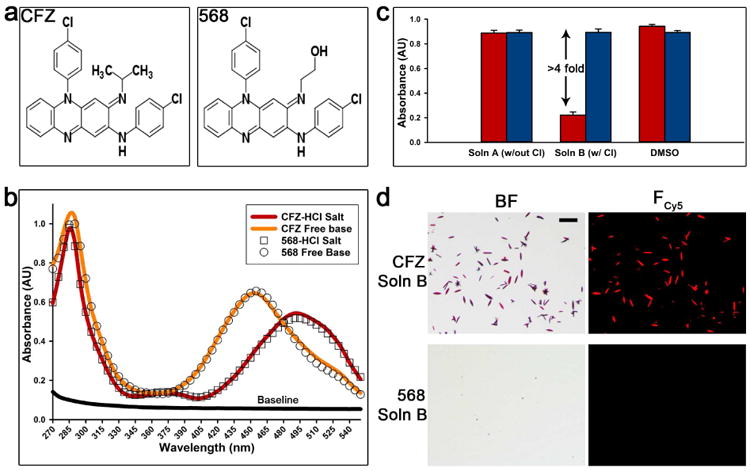
(a) The structural difference between CFZ and analog 568 at the tertiary amine is a specific substitution of the isopropyl group with a 2-hydroxyethyl. (b) The absorbance profiles (270-550nm) show the similarity of CFZ and analog 568 free base and hydrochloride salt forms, respectively. (c) The ability of both CFZ and analog 568 to precipitate as hydrochloride salt in simulated lysosomal conditions (pH 4.5). This was determined by measuring the absorbance (285nm) in different conditions: Soln A (no chloride), Soln B (100mM chloride), and DMSO (red = CFZ, blue = 568). (d) Hydrochloride salt precipitation in the presence of chloride (Soln B) was verified by brightfield (BF) and fluorescence microscopy (Fcy5). Scale bar = 50μm.
