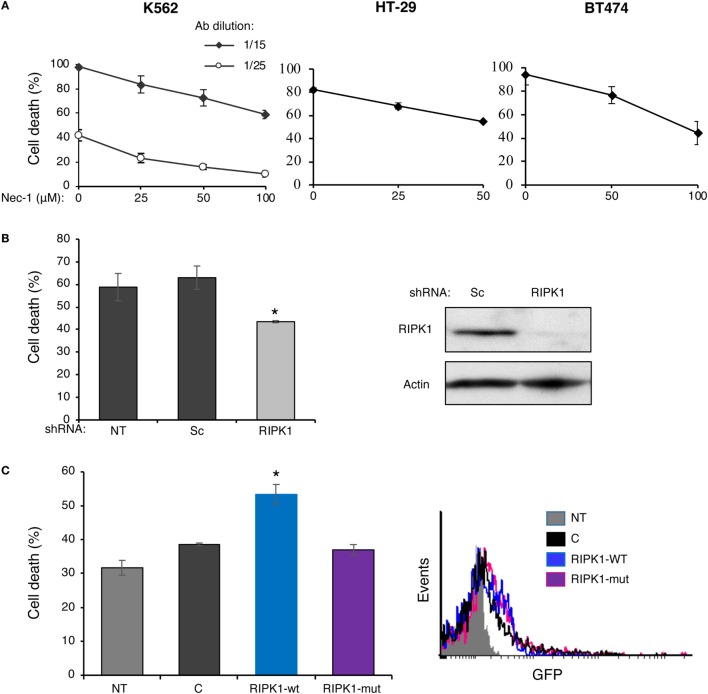
Figure 1.
Complement C5b-9 induces receptor-interacting protein kinase 1 (RIPK1)-dependent necrosis. (A) K562, HT-29, or BT474 cells were treated with necrostatin-1 (Nec-1) or with DMSO (0) as control for 1 h at 37°C. Cell death (CD) by antibody (30 min at 4°C) and complement (1 h at 37°C) was performed as described under Section “Materials and Methods.” The experiment with K562 cells was performed with two antibody (Ab) dilutions. The percentage of CD was analyzed by propidium iodide inclusion. Results of three independent experiments are expressed as the mean percentage of CD ± SD. The percentage of CD by Nec-1, antibody, and HIS was 3–7% (negative controls). Statistical analysis showed that Nec-1 significantly inhibited CD (one-way-ANOVA, P < 0.01). (B) K562 cells transfected for 48 h with RIPK1-shRNA, a scrambled (Sc) shRNA, or not transfected (NT) were treated with antibody and complement and the percentage of CD was determined as described in panel (A). Transfection with RIPK1-shRNA significantly inhibited the CD relative to the scrambled shRNA (t-test, P < 0.01). The RIPK1 expression level (relative to actin) in the transfected cells was assessed by Western blotting analysis. A representative blot is shown. (C) K562 cells were transfected with the GFP-tagged plasmids: wild-type RIPK1 (RIPK1-wt), RHIM-ALAA mutant (RIPK1-mut), an empty vector control (C), or were NT. After 52 h, the cells were treated with antibody and complement and the CD was determined as above. Transfection with RIPK1-wt significantly enhanced the CD relative to empty vector and RIPK1-mut (t-test, P < 0.01). Transfection efficiency was determined by analyzing the GFP expression by flow cytometry. A representative histogram is shown. All results represent three independent experiments.