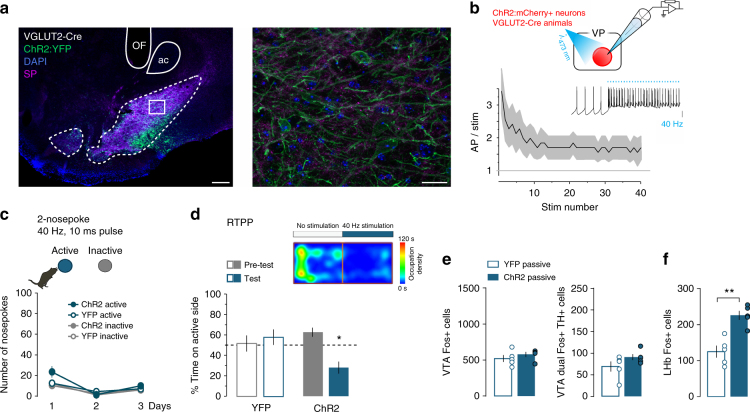
Fig. 4.
Stimulation of VP glutamate neurons induces place avoidance. a Expression of ChR2:YFP in the VP of VGLUT2-Cre mouse imaged under widefield (left, scale 200 µm) or apotome (right, scale 20 µm) illumination. b Action potential discharge of ChR2:mCherry+ VP glutamate neuron in response to 40-Hz photostimulation (n = 7 cells); SEM represented in gray. Inset shows representative trace; scale = 20 mV. c Over three daily 1-h two-nosepoke ICSS sessions, mice did not demonstrate robust self-stimulation for VP glutamate neurons (n = 5 YFP controls, n = 6 ChR2). d VGLUT2-Cre mice avoided the compartment paired with photostimulation of VP glutamate neurons in the RTPP assay (n = 5 YFP and ChR2 animals). Right panel shows occupation density of an example mouse during a test trial. e Passive activation of VP glutamate neurons failed to increase Fos+ cell counts in the VTA (n = 5). f However, the number of LHb cells positive for Fos increased following passive stimulation of VP glutamate neurons. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. See also Supplementary Figure 5