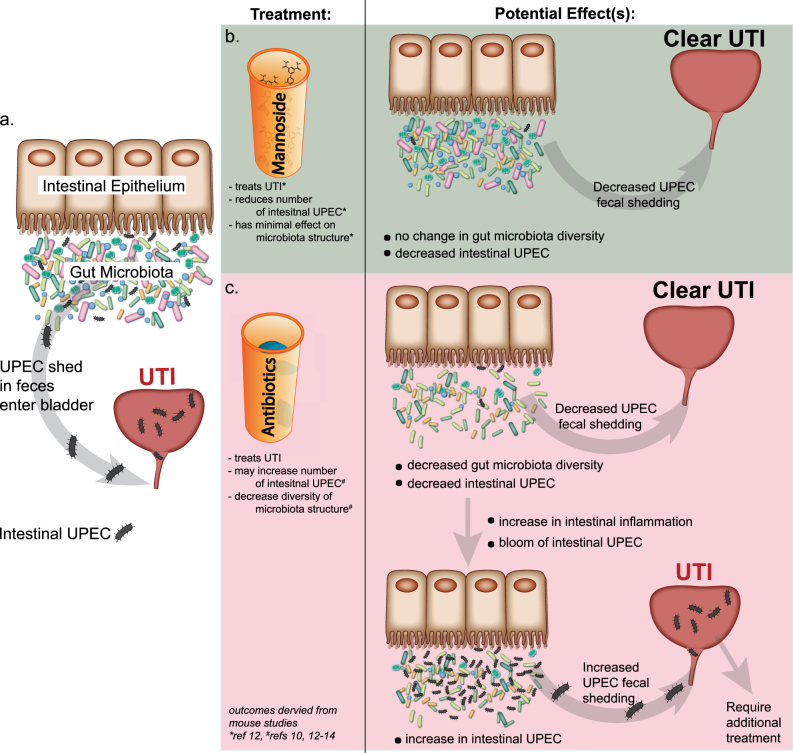
Fig. 1.
Potential effects of oral mannoside and antibiotic treatment on the intestinal UPEC population. a Intestinal UPEC reach the bladder and can cause UTI after being shed in the feces. b Oral mannoside treatment targets and reduces the UPEC intestinal population and simultaneously treats and clears UTI in the bladder with minimal effects on the overall structure/diversity of the gut microbiota. c Conversely, oral treatment with clinically relevant broad-spectrum antibiotics, like ciprofloxacin, can treat and clear UTI but reduces the overall abundance and diversity of the gut microbiota. The resulting intestinal inflammation caused by antibiotic treatment may promote intestinal E. coli colonization (including UPEC) and thus can lead to increase UPEC fecal shedding, promoting recurrent UTI