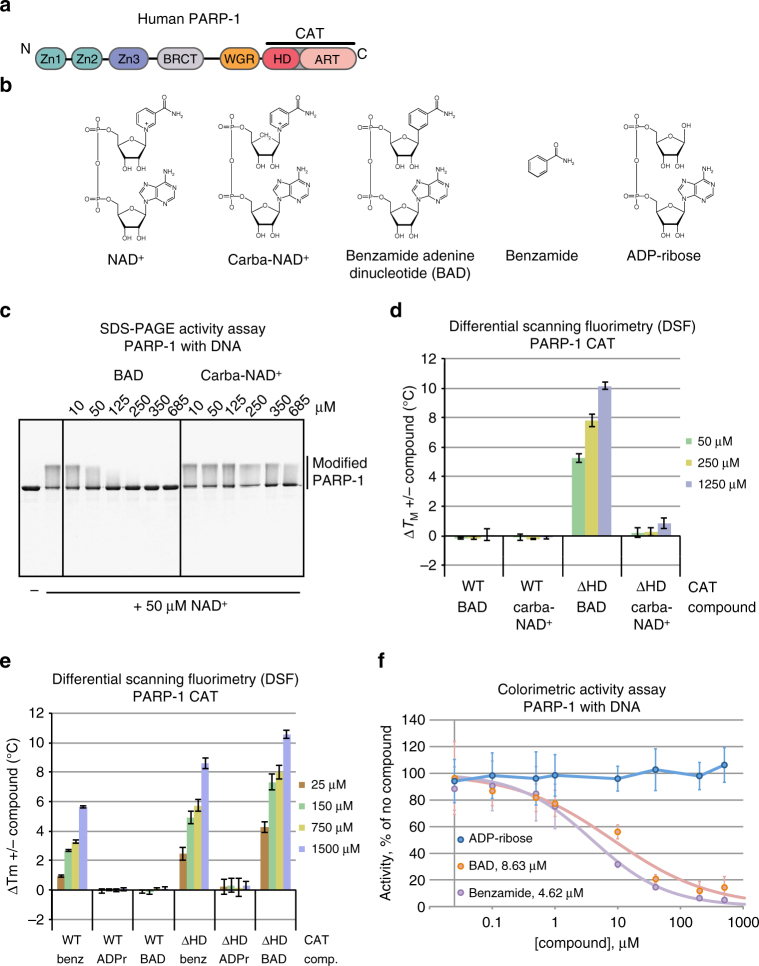
Fig. 1.
Non-hydrolyzable NAD+ analog binding and inhibition of PARP-1. a Schematic representation of PARP-1 domains. b Chemical structure of key compounds used in this study: NAD+, non-hydrolyzable NAD+ analogs carba-NAD+ and benzamide adenine dinucleotide (BAD), benzamide, and ADP-ribose (ADPr). c SDS-PAGE PARP-1 activity assay (1 μM DNA, 1 μM protein, 50 μM NAD+) in the presence of carba-NAD+ and BAD. An image of the entire gel is included in Supplementary Fig. 10. d, e Differential scanning fluorimetry (DSF) experiment using PARP-1 CAT domain WT or ΔHD (5 μM) and various amounts of carba-NAD+, BAD, benzamide, and ADP-ribose. ΔTM is calculated by subtracting the TM and ΔTM obtained in the absence of compound from the TM obtained in the presence of compound. The experiments were all performed in triplicate for which averages and standard deviations are shown. f Colorimetric assay of full-length PARP-1 DNA-dependent activity in the presence of ADP-ribose, benzamide, and BAD using 20 nM PARP-1, 40 nM DNA (18-bp duplex) and 50 μM NAD+ (99:1, NAD+:bio-NAD+). Experiments were performed in quadruplicate and the averages and standard deviations for each compound concentration are shown, as well as the average IC50 values for benzamide and BAD