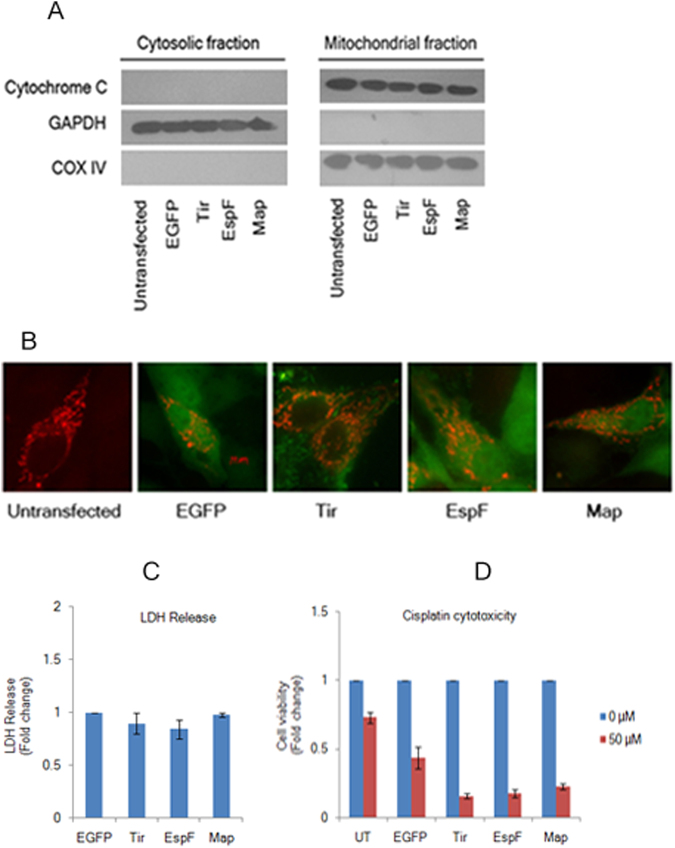
Figure 7.
Tight junction disruption by EspF and Map is independent of mitochondrial function. (A) Constitutive expression of EGFP-EspF and EGFP-Map does not cause the release of cytochrome c from the mitochondria. Cytosolic and mitochondrial fractions were isolated from untransfected, EGFP, EGFP-Tir, EGFP-EspF and EGFP-Map cell lines and analyzed by immuno-blotting with cytochrome c antibody. Equal loading on gels was confirmed by using COX IV as the mitochondrial marker and GAPDH as the cytosolic marker. Blots are representative of three independent experiments. Full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Figure S8. (B) Cells expressing EGFP-EspF and EGFP-Map display normal mitochondrial morphology. Cells from untransfected, EGFP, EGFP-Tir, EGFP-EspF and EGFP-Map cell lines were grown on glass cover-slips and transduced with CellLight Mitochondria-RFP, BacMam 2.0 reagent to label the mitochondria with RFP. Cells were imaged after 16 hours on a Zeiss ApoTome (Axiovert 40 CFL) using 63 × oil objective. (n = 3); scale: 10 µm. (C,D) Cytotoxicity of EspF and Map to MDCK cells. Cytotoxicity was assessed by measuring the amount of LDH released by EGFP, EGFP-Tir, EGFP-EspF and EGFP-Map cells into the culture medium. Fold changes in LDH release with respect to EGFP cells are depicted (C). Results are representative of three independent experiments. Confluent cultures of untransfected, EGFP, EGFP-Tir, EGFP-EspF and EGFP-Map cells were grown in the absence (0 µM) or presence (50 µM) of cisplatin to induce apoptosis (D). The number of viable cells was determined by MTT assay and fold change with respect to untreated cells was plotted for all cell lines. UT: Untransfected.