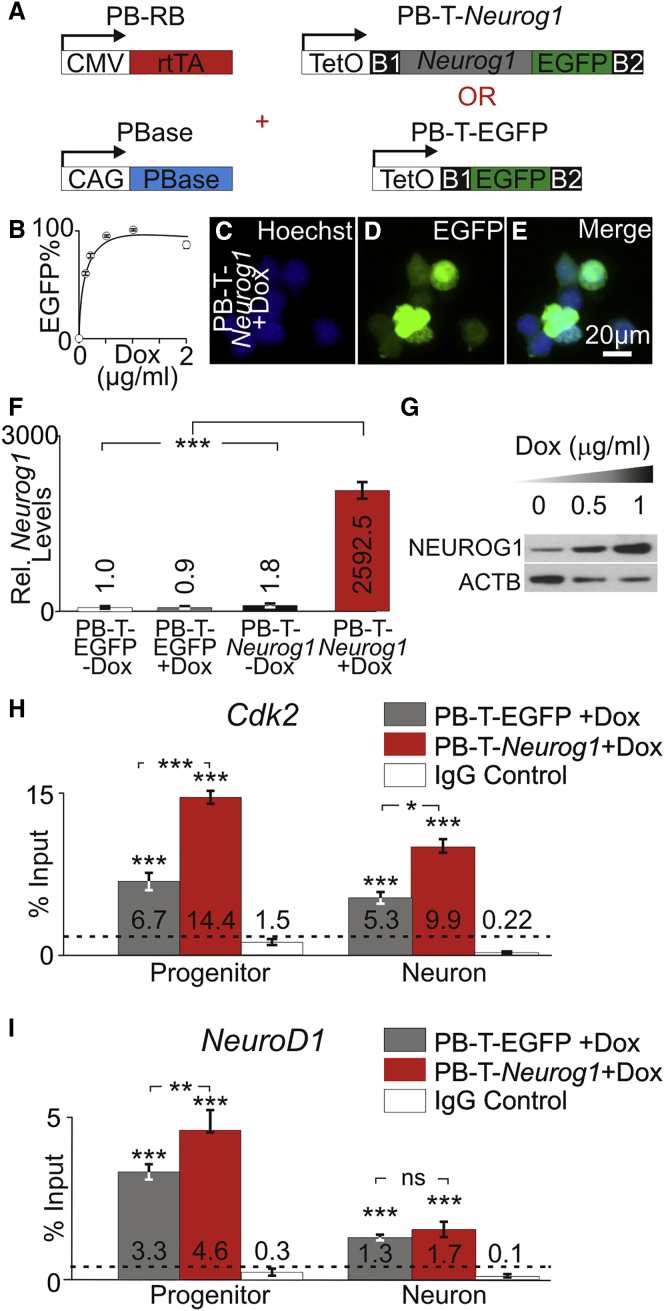
Figure 3.
Enrichment of NEUROG1 at Cdk2 and NeuroD1 Promoter
(A) PiggyBAC constructs for generating stable cell lines allow for inducible expression of Neurog1 IRES EGFP or EGFP. Constructs with TetO driving Neurog1 IRES EGFP or EGFP were co-transfected with a rtTA construct (PB-RB). Transient expression of the transposase using the PBase allowed stable integration of plasmid sequence and generation of inducible stable iMOP cell lines PB-T-EGFP and PB-T-Neurog1.
(B) Percentage of EGFP-expressing cells were quantified in PB-T-Neurog1 cultures at different doxycycline (Dox) concentrations (n = 5 for each concentration).
(C and D) Hoechst (C) and EGFP (D) fluorescence of PB-T-Neurog1 cells after induction with 1 μg/mL Dox.
(E) Merged image showed that the vast majority of cells express EGFP (n = 3).
(F) Relative Neurog1 transcript levels in PB-T-EGFP and PB-T-Neurog1 cells cultured in the presence or absence of 1 μg/mL Dox (n = 3 for each condition).
(G) Western blot of NEUROG1 protein levels with increasing Dox concentrations (n = 3 for each condition).
(H and I) ChIP-qPCR using NEUROG1 antibody in PB-T-EGFP and PB-T-Neurog1 cells after Dox induction at the (H) Cdk2 and (I) NeuroD1 promoter regions for proliferating progenitors and iMOP-derived neurons (n = 3 for each condition).
Error bars denote ±SEM. ns, not significant; ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.