Figure 2.
DNA Transgene Expression Vectors and Regulatory Mechanisms
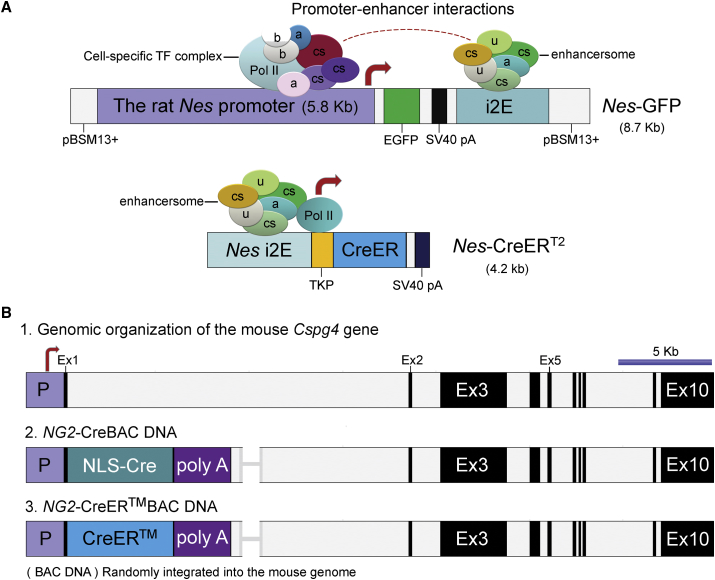
(A) Transgene expression vectors based on the rat Nes gene. Top panel: Nes-GFP, subcloned into the pBSM13 vector, contains the 5.8-kb rat Nes promoter and the 1.8-kb neural-specific intron-2 enhancer fragment (i2E), which flanked the enhanced version of GFP (EGFP). The 8.7-kb final construct, mimicking the arrangement of the regulatory sequences of the Nes or NES found in the rat, mice, and humans, was used for the pronuclear injections of the fertilized oocytes (Mignone et al., 2004). Lower panel: Nes-CreERT2 comprises the T2 mutant form of a Cre recombinase-estrogen receptor fusion (Cre-ERT2) (Feil et al., 1997) under the control of a thymidine kinase promoter (TKP) driven by the 1.8-kb i2E as described in the top panel (Balordi and Fishell, 2007). In Nes-GFP transgenic mice, a cell-specific transcriptional complex at the promoter might interact with the neural-specific intron-2 enhancersome, thereby mediating different gene expression patterns in miscellaneous cell types including BM cells. However, in the case of Nes-CreERT2 mice, the transgene is largely driven by the intron 2 enhancersome.
(B) Transgene expression vectors based on the chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan four gene (Cspg4), also known as NG2 (neural/glial gene). (1) Genomic organization of the Cspg4 gene is based on the recent genomic information from the NCBI sequence (NM_1390012) with a scale bar (5 kb). (2 and 3) NG2-CreBAC (Zhu et al., 2008) and NG2-CreER™BAC (Zhu et al., 2011) DNAs were used for generating NG2-Cre and NG2-CreER™ transgenic mice, respectively. In brief, a 208-kb mouse bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) containing the entire Cspg4 gene was modified by introducing a Cre recombinase cDNA with a nuclear localization signal (NLS) or a CreER™ cDNA (Danielian et al., 1993, Littlewood et al., 1995) into exon 1 of the Cspg4 gene, followed by a rabbit β-globin polyadenylation sequence, poly(A). These two transgenes were microinjected into the pronucleus of fertilized oocytes from C57BL/6J mice to generate the transgenic lines of interest.
a, adaptor protein(s); b, basal transcriptional factor(s); Cre-ERT2, Cre recombinase fused to the human estrogen receptor ligand-binding domain with a triple mutation (i.e., G400V/M543A/L544A), which does not bind its natural ligand (17β-estradiol); Cre-ER™, Cre recombinase fused to a G525R mutant form of the mouse estrogen receptor ligand-binding domain; cs, cell-specific, Ex, exon; i2E, the intron 2 enhancer fragment of the rat Nes gene; P, promoter; Pol II, RNA polymerase II; SV40 pA, the polyadenylation sequences from the simian virus 40; TF, transcriptional factor; TKP, a 160-bp herpes simplex virus (HSV) thymidine kinase (TK) promoter; u, unidentified factor(s).