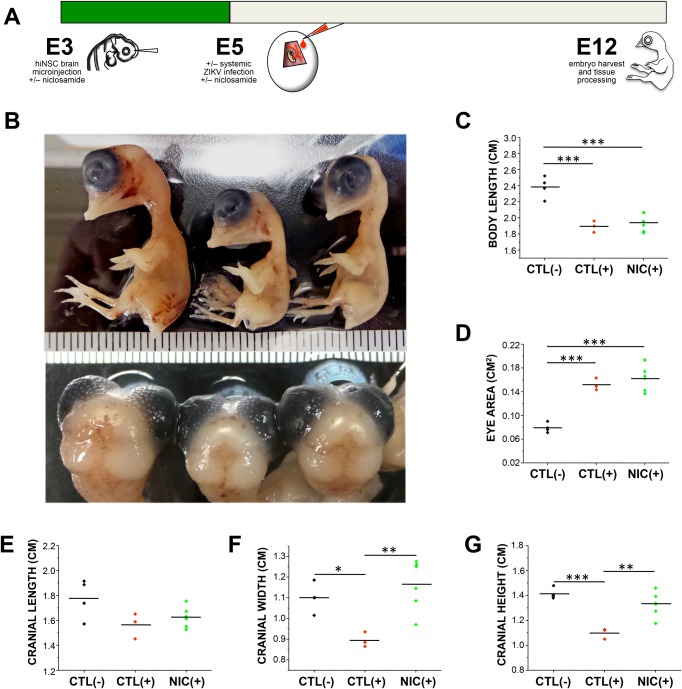
Fig. 3.
Systemic Niclosamide treatment can partially rescue ZIKV-induced reduction in cranial size in a humanized in vivo model. (A) Schematic diagram showing experimental timeline of injection of hiNSCs as well as systemic ZIKV infection and NIC treatment. Briefly, embryos were injected with hiNSCs intracranially and treated with the first dose of either vehicle or NIC via the CAM at E3. At E5, embryos were subjected to systemic ZIKV infection as well as the second dose of either vehicle or NIC via the CAM, and all embryos were harvested at E12. (B) Image of E12 embryos after treatment (left to right: Mock plus vehicle, ZIKV plus vehicle, ZIKV plus NIC). Quantification of body length (C), eye area (D) as well as morphological features of the cranium including length (E), width (F) and height (G) across treatments. *P≤0.05, **P≤0.01, ***P≤0.001; as determined by one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey test.