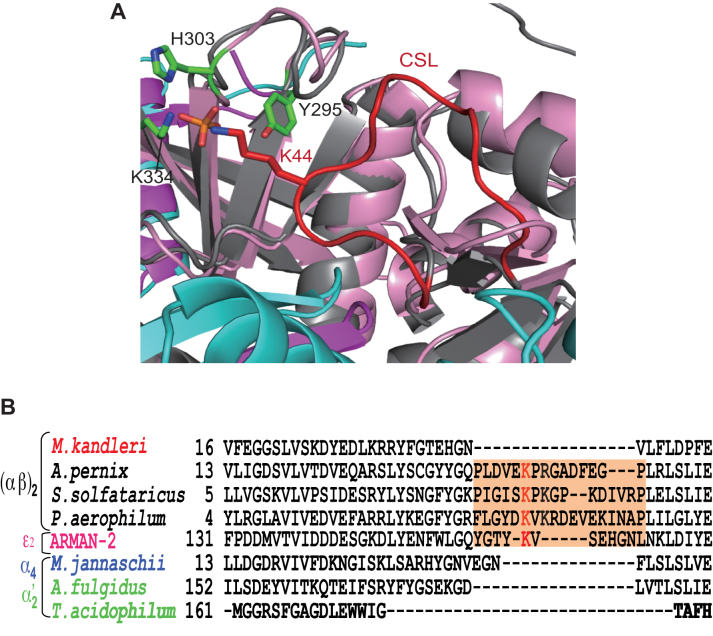
Figure 5.
Structural and sequence positioning of specific loops responsible for broad substrate specificity. (A) Superimposition diagram of Cα atoms of the α subunit (gray) in APE EndA onto that of the α unit (magenta) in fMKA EndA. The three catalytic residues (Y295, H303, and K334) are shown by a green stick model. The conserved K44 residue in the CSL (red) is depicted as a red stick model. (B) Amino acid sequence alignment of α subunits around the CSL region (highlighted in orange). Full names of the archaeal species are as follows: Methanopyrus kandleri, Aeropyrum pernix, Sulfolobus solfataricus, Pyrobaculum aerophilum, Candidatus Micrarchaeum acidiphilum (ARMAN-2), Methanocaldococcus jannaschii, Archaeoglobus fulgidus and Thermoplasma acidophilum. The key Lys residues responsible for broad substrate specificity are shown in red.