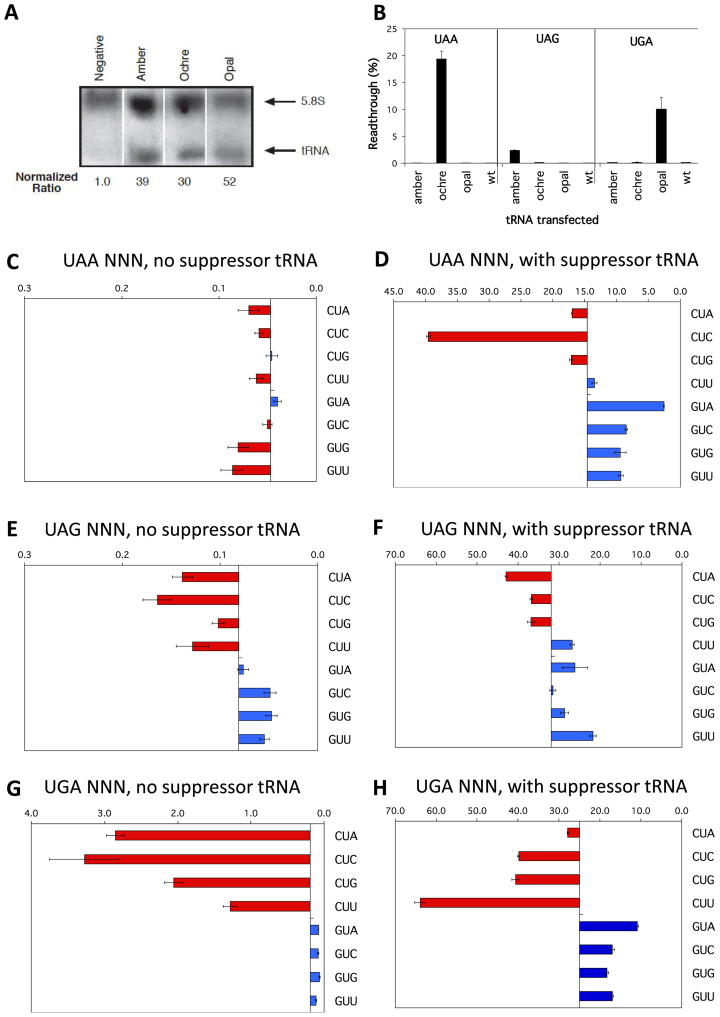
Figure 7.
Competition by cognate tRNAs at termination signals. (A) Northern blot probed for sup-tRNA (lower arrow) and 5.8S rRNA (upper arrow) transcripts. Expression levels of sup-tRNA relative to 5.8S rRNA are indicated. The sup-tRNA probe was able to detect ptRNA amber, ptRNA ochre and ptRNA opal as it was complementary to the anticodon loop of the tRNA, but degenerative for the specific anticodon sequence. (B) Termination efficiencies of the +1UAAAGA+6, +1UAGAGA+6 and +1UGAAGA+6 sequence contexts measured in COS-7 cultured cells co-transfected with cognate sup-tRNAs ptRNAoc (ochre UAA), ptRNAam (amber UAG), or ptRNAop (opal UGA); or with the parent control ptRNAser (wild-type tRNAser). Readthrough (%) was calculated by comparison to near-cognate control constructs (CAG/UAA, UAU/UAG, and UGG/UGA) and plotted on the x-axis. Presentation and replicates are as in Figure 2. (C-H) Termination efficiencies of selected UAA (C, D), UAG (E, F) and UGA (G, H) sequence contexts were measured in COS-7 cultured cells co-transfected with cognate suppressor tRNAs (right panels) or without (left panels). UAA sequence contexts were co-transfected with ptRNAoc (ochre UAA), UAG sequence contexts were co-transfected with ptRNAamber (amber UAG), and UGA sequence contexts were co-transfected with ptRNAop (opal UGA). Readthrough (%) was calculated as before. Results are graphed relative to the median termination efficiency for the series (without and with suppressors respectively: 0.047% and 14.61% UAA, 0.081% and 31.94% UAG, 0.190% and 25.0% UGA). Presentation, replicates and error bars were as before.