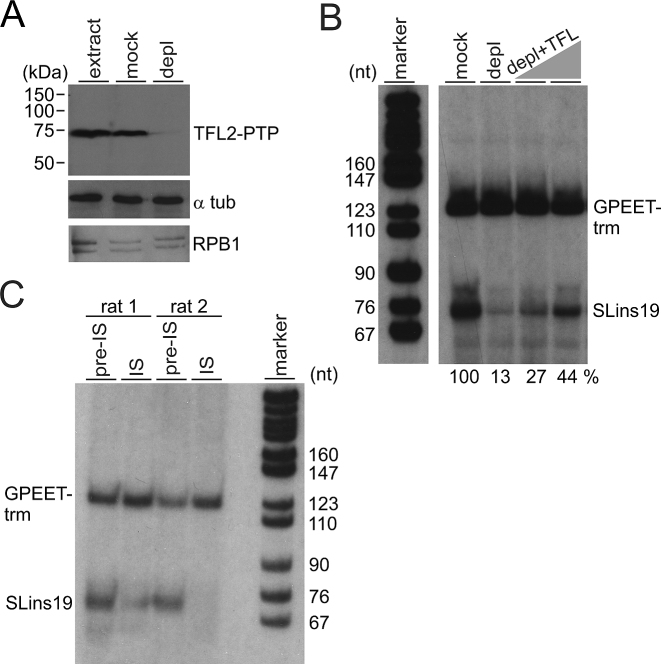
Figure 5.
TFL is essential for SLRNA transcription in vitro. (A) Immunoblot of extract from TbT2PTPee trypanosomes that was untreated (extract), mock-treated or TFL2-PTP-depleted (depl), detecting TFL2-PTP, α tubulin (α tub) and RNA pol II subunit RPB1 with specific antibodies. (B) Cotranscription of the SLRNA promoter template SLins19 and the RNA pol I-transcribed template GPEET-trm in mock-treated and TFL2-PTP-depleted extract. The latter reaction was reconstituted with 2 and 4 μl of sucrose gradient fraction 8 shown in Figure 4D. GPEET-trm and SLins19 RNA were detected by primer extension reactions using radiolabeled oligonucleotides that specifically hybridized to these RNAs. Extension products were separated on 50% urea/6% polyacrylamide gels and visualized by autoradiography. The correct length of the extension products verified correctly initiated transcription. Numbers at the bottom show the relative SLins19 signal strengths normalized by those of the GPEET-trm signals as determined by densitometry. The signal in mock-treated extract was arbitrarily set to 100. The pBR322-MspI marker lane on the left was derived from the same gel. (C) Cotranscription reactions were carried out in extract that was either mixed with pre-immune serum or anti-TFL2 immune serum derived from two different rats.