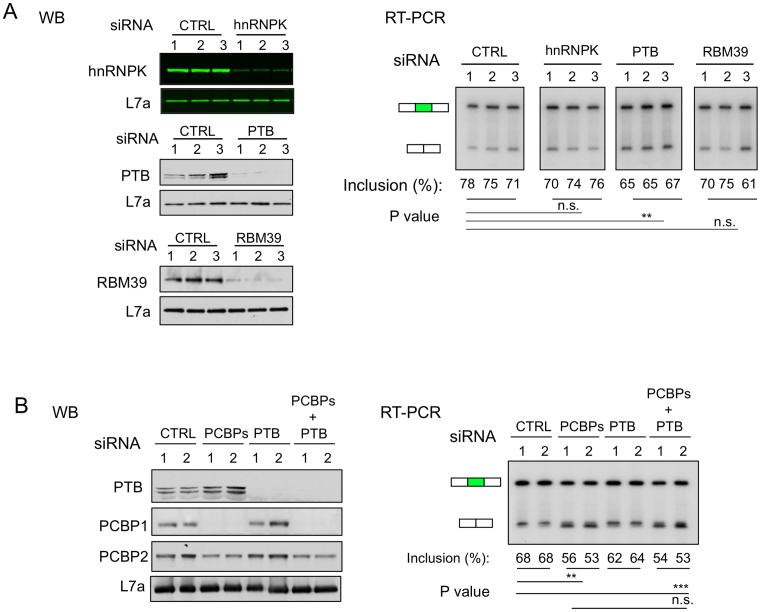
Figure 3.
Impact of three additional polypyrimidine binding proteins, hnRNPK, PTB, and RBM39 on CDK2 ex5 splicing. (A) Impact of targeted depletions hnRNPK, PTB, or RBM39 on CDK ex5 splicing. K562 cells were individually transfected with 3 distinct siRNAs targeting the mRNAs that encode each of the indicated proteins. Left: Depletions of individual proteins were confirmed by WB. Ribosomal protein L7a serves as a loading control. Right: The impact of targeted depletions on CDK2 ex5 splicing. Quantification and statistics of the gel are shown at the bottom of the corresponding lanes. n = 3. ∗∗P < 0.01, n.s.: not significant. (B) Impact of dual depletion of PCBPs and PTB on CDK2 ex5 splicing. K562 cells were transfected individually with PCBPs siRNA (siRNA PCBP1/2-2), or PTB siRNA cocktail (mixture of the 3 PTB siRNAs used in Figure 3A), or combination of PCBPs and PTB siRNAs, along with negative control (CTRL), in biological replicates (n = 2). Left: Western blot confirmations of efficient targeted protein depletions. Right: Impact of targeted depletions on CDK2 ex5 splicing as assessed by RT-PCR. Quantification and statistics of the gel were shown at the bottom. ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001, n.s.: not significant. n = 2.