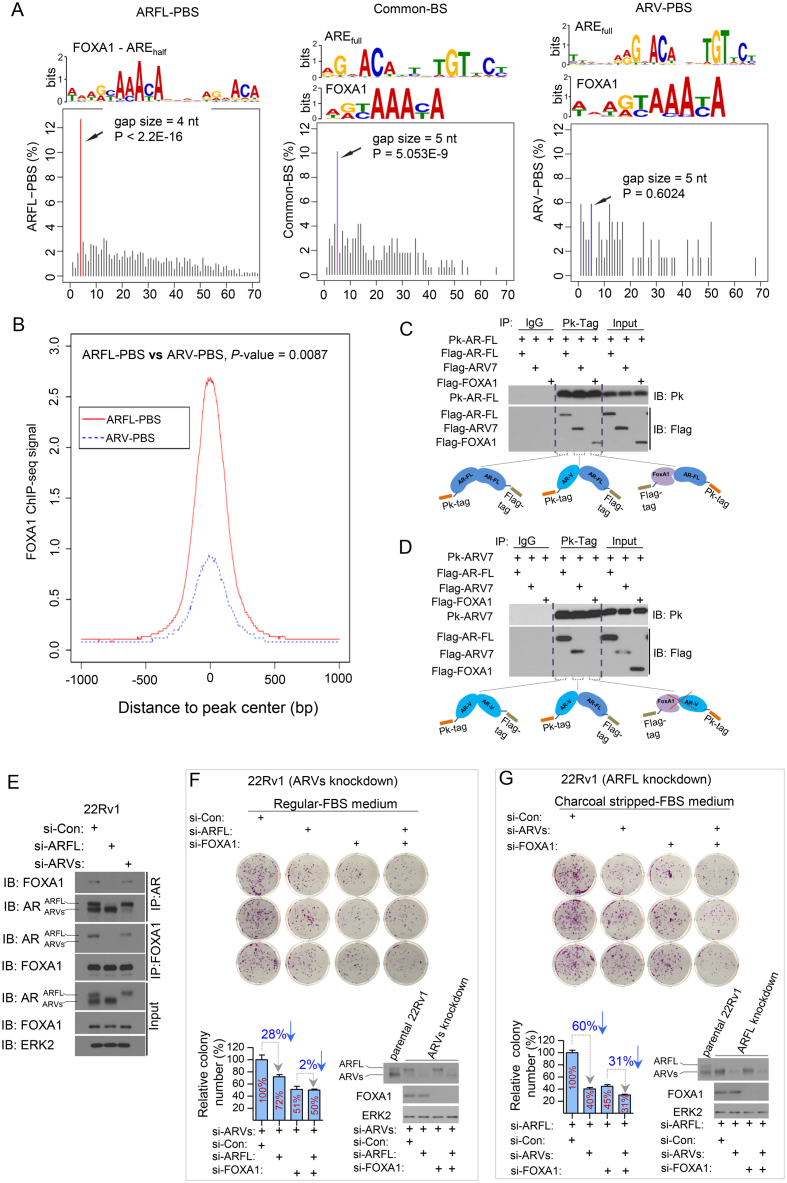
Figure 3.
Cistrome characteristics of ARV-PBS, ARFL-PBS and Common-BS. (A) DNA motifs and frequency spectrum of gap sizes between AREfull and FOXA1 motif identified from ARFL-PBS, Common-BS and ARV-PBS loci. (B) FOXA1 ChIP-seq signal profiles for ARV-PBS and ARFL-PBS in 22Rv1 cells. 22Rv1 cells were treated with the synthetic androgen R1881 (methyltrienolone) for 24 h and samples were utilized for FOXA1 ChIP-seq analysis. FOXA1 binding signal at ARFL-PBS was significantly higher than that at ARV-PBS (P = 0.0087, two-tailed Wilcoxon rank sum test). (C and D) Human 293T cells were transfected with Pk-tagged (V5-Tag) ARFL (Pk-ARFL) or Pk-tagged AR splice variant 7 (Pk-ARV7) followed by cell lysis and Pk-tag antibody immunoprecipitation. Detected protein interactions were illustrated in both (C) and (D). (E) 22Rv1 cells transfected with siRNA targeting AR exon 7/8 to knock down ARFL or with siRNAs targeting AR-V1/V3/V4/V7 to knock down AR variants for 48 h followed by cell lysis and immunoprecipitation with AR-N20 or FOXA1 antibody. The effect of siRNA-mediated AR silencing and the protein interactions between FOXA1 and ARFL or ARVs were examined using western blots. (F and G) ARV-knockdown (F) or ARFL-knockdown 22Rv1 cells (G) were transfected with control siRNA (si-Con) or siRNA targeting ARFL or FOXA1 alone or in combination (F) or siRNAs for ARVs or FOXA1 alone or in combination (G), and then cells were seeded in 35-mm dishes (3,000 cells/dish). The ARFL knockdown 22Rv1 cells were cultured with charcoal stripped-FBS medium to further inactivate ARFL. After 10 days, cells were fixed and stained with crystal violet, and the colony number in every group was counted (n = 3). The colony numbers were normalized to the control siRNA group.