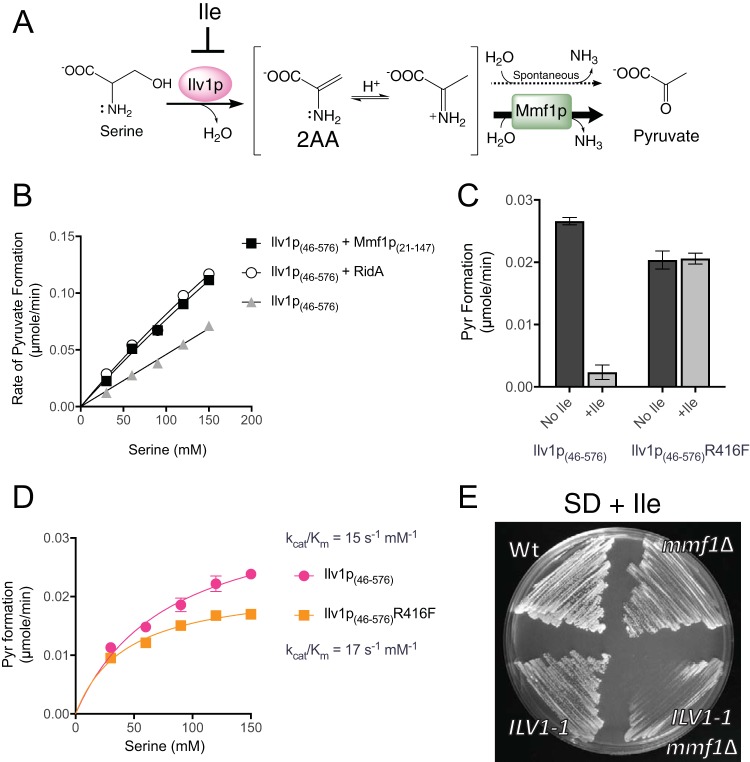
FIG 2 .
Ilv1p generates 2AA stress in yeast lacking Mmf1p. (A) Scheme of Ilv1p-mediated pyruvate formation, showing 2AA as an unbound intermediate that can be hydrolyzed to pyruvate by solvent water or Mmf1p. Isoleucine allosterically inhibits Ilv1p activity and prevents 2AA formation. Cha1p catalyzes the same reaction as Ilv1p but is not allosterically regulated. (B) The rates of conversion of serine to pyruvate by Ilv1p(46−576) were enhanced similarly by adding Mmf1p(21−147) (S. cerevisiae) or RidA (S. enterica). Data represent averages and standard deviations of results from three independent experiments, with error bars not exceeding the symbol boundaries. (C) The serine dehydratase activity of the purified Ilv1p(46−576)-R416F variant was insensitive to a concentration of isoleucine (3.3 mM) that completely inhibited the wild-type enzyme. Data represent averages and standard deviations of results from three independent experiments. (D) Ilv1p(46−576)-R416F has levels of catalytic efficiency for serine dehydration similar to those seen with the wild-type enzyme. Data indicate averages and standard deviations of results from three independent experiments. (E) Inserting the ILV1-1 allele encoding Ilv1pR416F into a ρ0 mmf1Δ strain prevented isoleucine from restoring full growth to the double mutant compared to the ρ° mmf1Δ single mutant following 48 h of incubation on solid medium consisting of SD plus Ile (SD + Ile) (1 mM) at 30°C. Wt, wild type.