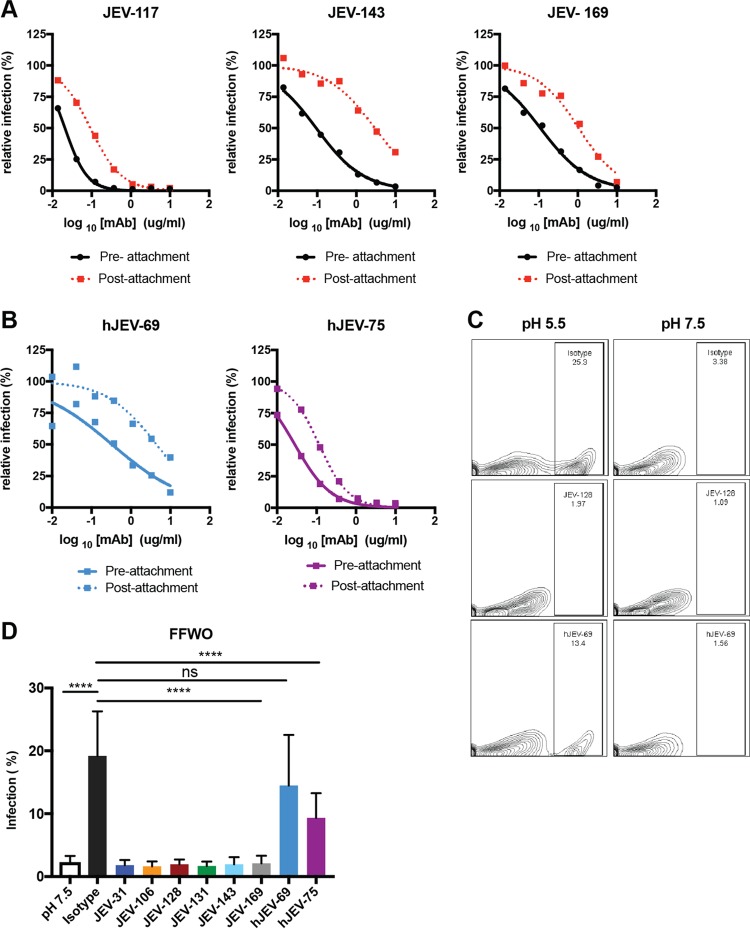
FIG 2 .
Mechanism of neutralization by anti-JEV MAbs. (A and B) The preattachment inhibition assay (solid lines) was performed by incubating 102 FFU of JEV-SA14-14-2 with serial dilutions of MAbs starting at 10 µg/ml for 1 h at 4°C before addition to prechilled Vero cells at 4°C and subsequently following the FFA protocol. The postattachment assay (dashed lines) was performed by adding 102 FFU of JEV-SA14-14-2 to cells for 1 h at 4°C. After extensive washing to remove unbound virus, serial dilutions of MAbs were added, starting at 10 µg/ml, and incubated for 1 h at 4°C, and the FFA then was completed at 37°C. Data are representative of three experiments performed in triplicate. (C) The fusion-from-without (FFWO) assay was performed after incubating Vero cells at 4°C with JEV-SA14 (MOI of 50) for 2 h. For these experiments, we used JEV-SA14 instead of JEV-SA14-14-2 because it could be grown to a higher titer. Cells were washed extensively, and the indicated MAbs were added for 30 min. Plasma membrane fusion was induced by exposing the cells briefly (~7 min) to an acidic pH buffer. After pH normalization, cells were incubated with 10 nM concanamycin for 24 h to inhibit infection via the endosomal pathway and collected, fixed, permeabilized, and stained for E protein expression. The treatment and percentage of positive cells are shown. (D) The data are pooled from three independent experiments, each performed in triplicate, with error bars (standard deviation) and were analyzed using one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons to the isotype control condition. ****, P < 0.0001; ns, not significant.