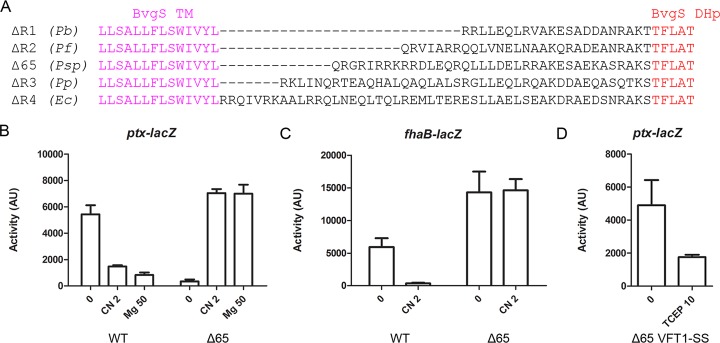
FIG 2 .
Chimeric BvgS variants with natural X linkers of homologs. (A) Sequences of the variants in which the region between the TM segment and the DHp domain of BvgS was replaced with natural linkers of PAS-less BvgS homologues. The species from which the sequences originated are Pseudomonas brassicacearum (accession no. WP_039012684; Pb), Pseudomonas fragi (accession no. WP_016782378; Pf), Pseudomonas sp. strain M1 (accession no. WP_009621264; Psp), Pseudomonas putida (GenBank accession no. AAN69015; Pp), and Enterobacter cloacae (accession no. WP_050860054; Ec). The variants obtained were BvgSΔR1, BvgSΔR2, BvgSΔ65, BvgSΔR3, and BvgSΔR4, respectively. (B and C) The ptx-lacZ (B) and fhaB-lacZ (C) reporters were used to determine the basal activities and the responses to 2 mM chloronicotinate (CN 2) or 50 mM MgSO4 (Mg 50) for the BvgSΔ65 variant compared to those of wt BvgS (WT). AU, arbitrary units. (D) The ptx-lacZ reporter was used to determine the effect of VFT1 domain closing on activity (BvgSΔ65 VFT1−SS variant). Where indicated, the reducing agent Tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine hydrochloride (TCEP) was added to the cultures at 10 mM to reduce the S-S bond in VFT1. The means and standard errors of the means are given.