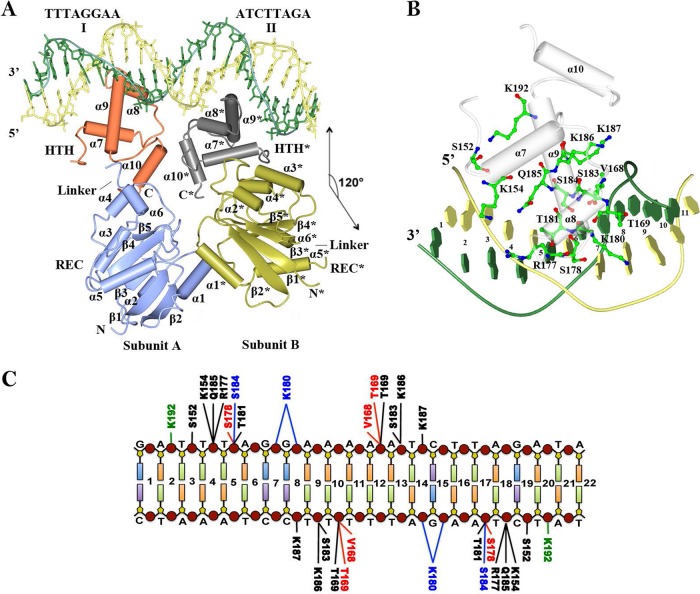
FIG 2 .
Structure of the RcsB-DNA complex. (A) Structure of the RcsB homodimer bound to DNA22. The rotational two-fold axis of symmetry in the dimer of REC and HTH domain are shown as coordinate axes x and z at a 120°. The secondary structure elements are labeled (marked with an asterisk for subunit B). The main and complementary strands of DNA are shown in yellow and green, respectively. (B) RcsB HTH domain (worms/tubes) bound to half-site I of DNA22 (worms/blocks). The residues involved in interactions are shown as balls and sticks. (C) Summary of interactions between RcsB residues and DNA nucleotides (indicated by lines). Hydrogen bonds (H-bonds) between protein side chains and DNA bases are shown in blue, H-bonds between main chains and phosphates of DNA are shown in red, and H-bonds between side chains and phosphates of DNA are shown in black. The electrostatic interactions (<3.8 Å) between RcsB and DNA are shown in green.