FIG 4 .
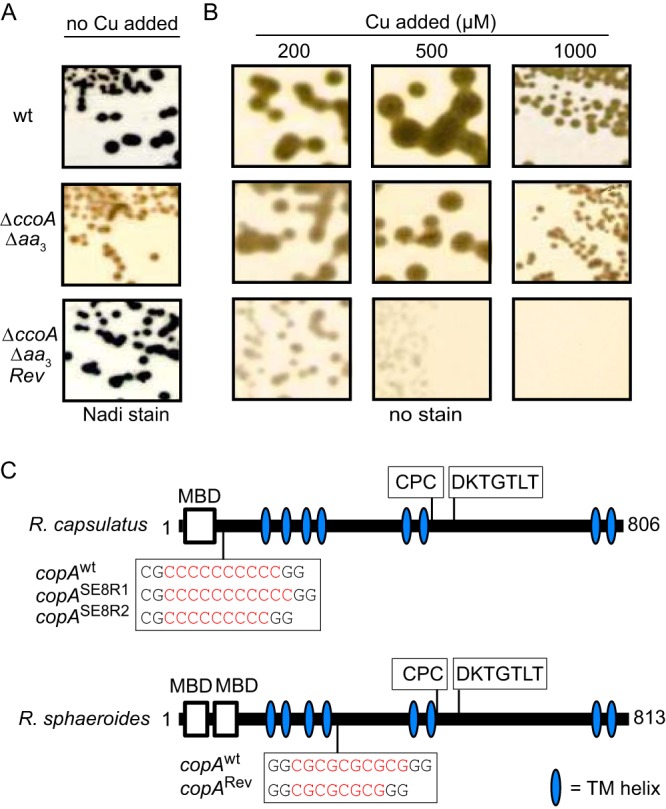
Bypass suppressors of R. sphaeroides mutants lacking CcoA are located in CopA and regain cbb3-Cox activity at the expense of Cu2+ hypersensitivity. (A) Spontaneous NADI+ bypass suppressors ΔccoA Δaa3/Revi that regained cbb3-Cox activity were isolated from the ΔccoA Δaa3 mutant. (B) The ΔccoA Δaa3/Revi suppressors exhibit hypersensitivity to Cu2+ compared with the wild type (wt) and the ΔccoA Δaa3 mutant. (C) The suppressor mutations corresponded to 2-bp (CG) deletions in copA (RSP_2829) of R. sphaeroides in a stretch of five CG repeats located immediately after the fourth transmembrane segment. They are compared with similar CcoA suppressors (CopASE8R1 and CopASE8R2) isolated previously from R. capsulatus (32). The latter mutations corresponded to a single-base-pair (C) indel located in a stretch of 10 C repeats of R. capsulatus CopA before its first transmembrane helix. In both species, the suppressor mutations led to translational frameshifts that abolished CopA activity, leaving intact the possibility of producing N-terminally truncated polypeptides that still carry the MBDs. The N-terminal MBD, the phosphorylation domain (DKTGT), and the transmembrane metal binding motif (CPC) are represented in CopA.
