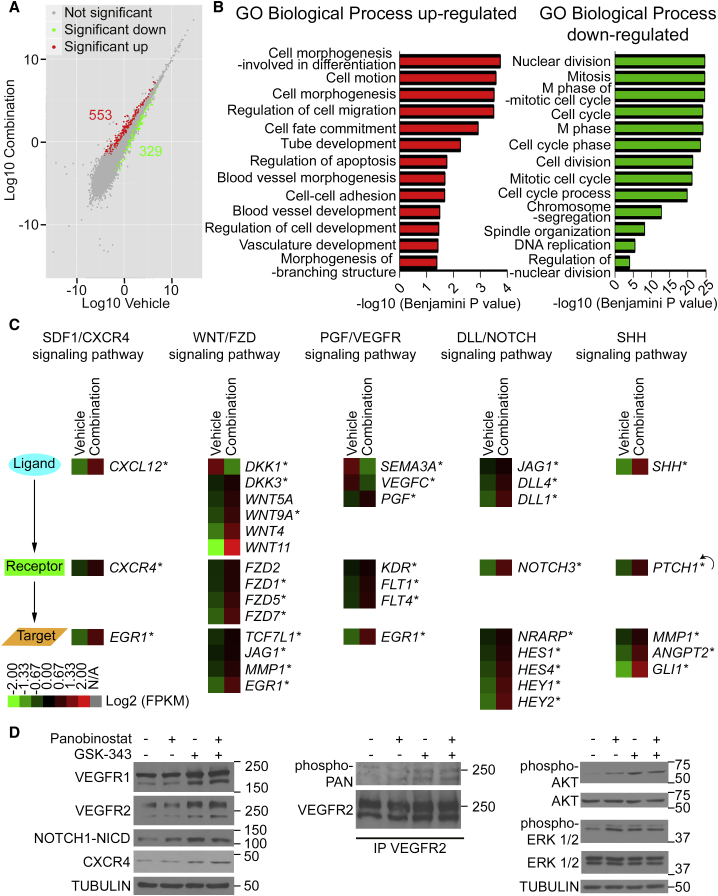
Figure 2.
Pharmacologic Treatment of ECFCs with a Combination of EZH2 and HDAC Inhibitors Activates Multiple Pro-angiogenic Pathways Simultaneously
(A) Global changes in gene expression upon drug treatment versus vehicle treatment analyzed by RNA-seq. Scatterplot shows upregulated (red) and downregulated (green) genes (n = 3).
(B) Representative Gene Ontology (GO) Biological Process categories significantly enriched for up- and downregulated genes in ECFCs treated with GSK-343 and panobinostat.
(C) Heatmaps of up- and downregulated genes that belong to the indicated signaling pathways as identified by RNA-seq analysis and validated by qRT-PCR (∗). Data are expressed in log2(FPKM) (n = 3). The feedback arrow indicates a gene belonging to both receptor and target gene categories.
(D) Validation of cell-signaling pathway activation upon drug treatment at the protein level. Left: western blot analysis of ECFC extracts shows an increase in global protein levels of VEGFR1 (FLT1), VEGFR2 (KDR), cleaved intracellular domain of NOTCH1 (NOTCH1-NICD), and CXCR4 upon drug treatment. Middle: western blot analysis of VEGFR2 immunoprecipitates (IP) shows an increase in phospho-VEGFR2 upon drug treatment. Right: western blot analysis of ECFC extracts shows an increase in phospho-AKT and phospho-ERK1/2 upon drug treatment. Tubulin is used as a loading control. Molecular masses are indicated in kDa.
See also Figures S3 and S4 as well as Tables S1 and S2.