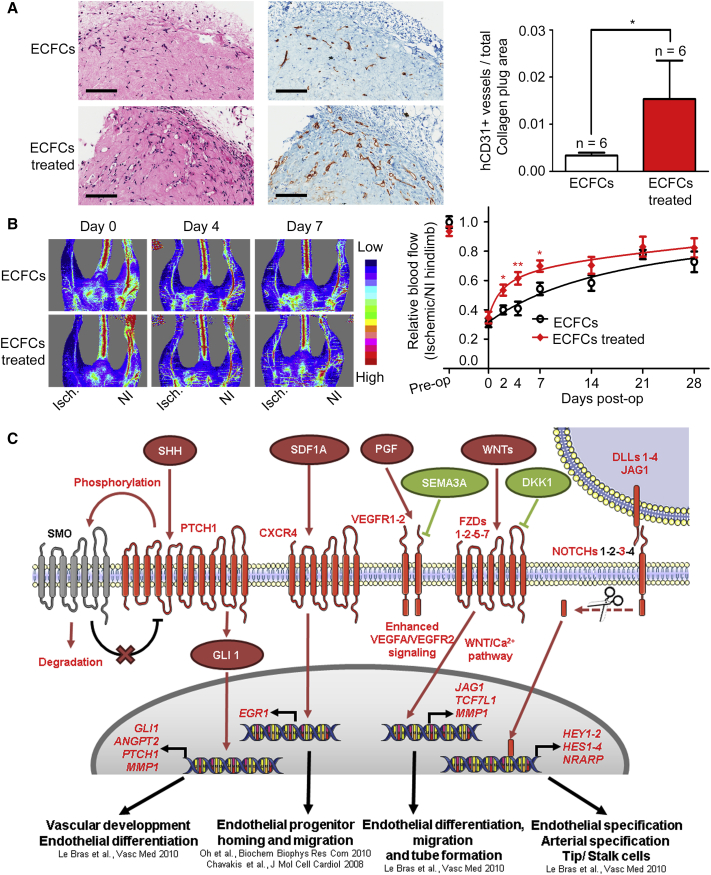
Figure 6.
Pharmacologic Treatment with a Combination of EZH2 and HDAC Inhibitors Accelerates Vasculogenesis and Blood-Flow Recovery by Transplanted ECFCs in a Mouse Model of Hindlimb Ischemia
(A) H&E staining (left) and anti-human (h) CD31 staining (right) identify ECFCs that have formed micro-capillaries in collagen gels after 3 weeks of implantation in mice (scale bar, 200 μm). Numbers of fully closed ECFC-derived hCD31+ capillaries are indicated per measured explanted area as mean values ± SEM (n = 6 mice per group).
(B) Laser Doppler perfusion imaging was used to measure blood flow pre-operatively (pre-op), immediately after induction of hindlimb ischemia (day 0) and at the indicated time points after injection of ECFCs pretreated with vehicle or with the drug combination. Left: representative laser Doppler images (Isch., Ischemic leg; NI, non-ischemic leg). Right: perfusion ratios (Isch./NI) are indicated as mean values ± SEM (ECFCs: days 0–14, n = 7 mice; days 21–28, n = 3 mice. ECFCs treated: days 0–14, n = 8 mice; days 21–28, n = 4 mice).
(C) EZH2 and HDAC inhibitors upregulate multiple transduction pathways in ECFCs.
Schematic representation of cell-signaling molecules and processes that are upregulated (red) or downregulated (green) upon treatment of ECFCs with the GSK-343 and panobinostat combination.
∗∗p < 0.01; ∗p < 0.05. See also Figure S6.