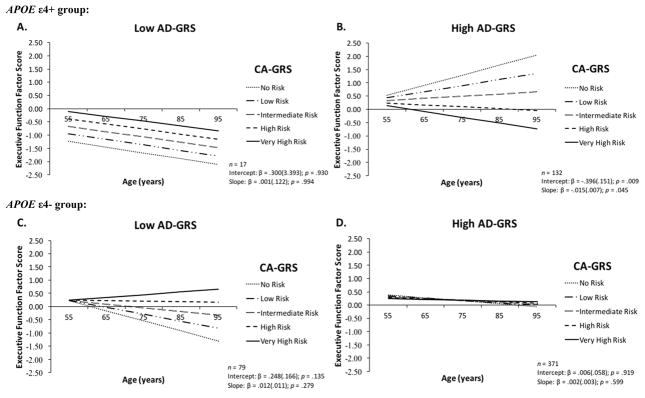
Figure 1.
Increasing risk associated with Cognitive Aging-Genetic Risk Score [CA-GRS: Catechol-O-methyltransferase + Brain-derived neurotrophic factor] was magnified by high Alzheimer’s disease-Genetic Risk Score [AD-GRS: Clusterin + Complement receptor 1 + Phosphatidylinositol-binding clathrin assembly protein] selectively in Apolipoprotein E (APOE) ε4 carriers. (A) APOE ε4 risk carriers with low AD-GRS showed overall poorer EF performance and same rate of 9-year decline regardless of CA-GRS; (B) APOE ε4 risk carriers with high AD-GRS showed poorer EF performance at age 75 years and steeper 9-year decline with increasing CA-GRS; (C) APOE ε4− group with low AD-GRS did not show poorer EF performance at age 75 years or steeper 9-year decline with higher CA-GRS; (D) APOE ε4− group with high AD-GRS showed similar EF performance at age 75 years and 9-year decline for all levels in the CA-GRS.