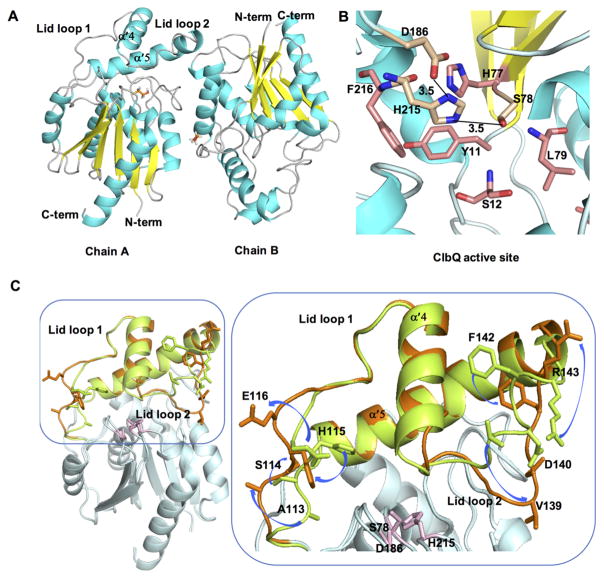
Figure 2.
Structure of ClbQ. (A) The asymmetric unit with two monomers of ClbQ, βME is shown as orange sticks. (B) The active site of ClbQ. The catalytic triad, Ser78, Asp186, and His215, are shown as gold sticks, the oxyanion hole (Ser12 and Leu79) and surrounding active site residues are colored salmon. (C) Superimposition of the chain A and chain B monomers. The core regions of both domains (cyan) is constant, and the flexible lid domains are represented (chain A, green; chain B, orange). Side chains of the residues on the flexible lid domain are labeled in the expanded view and the movement and orientations between the two monomers are depicted with blue arrows. The catalytic triad is shown as pink sticks.