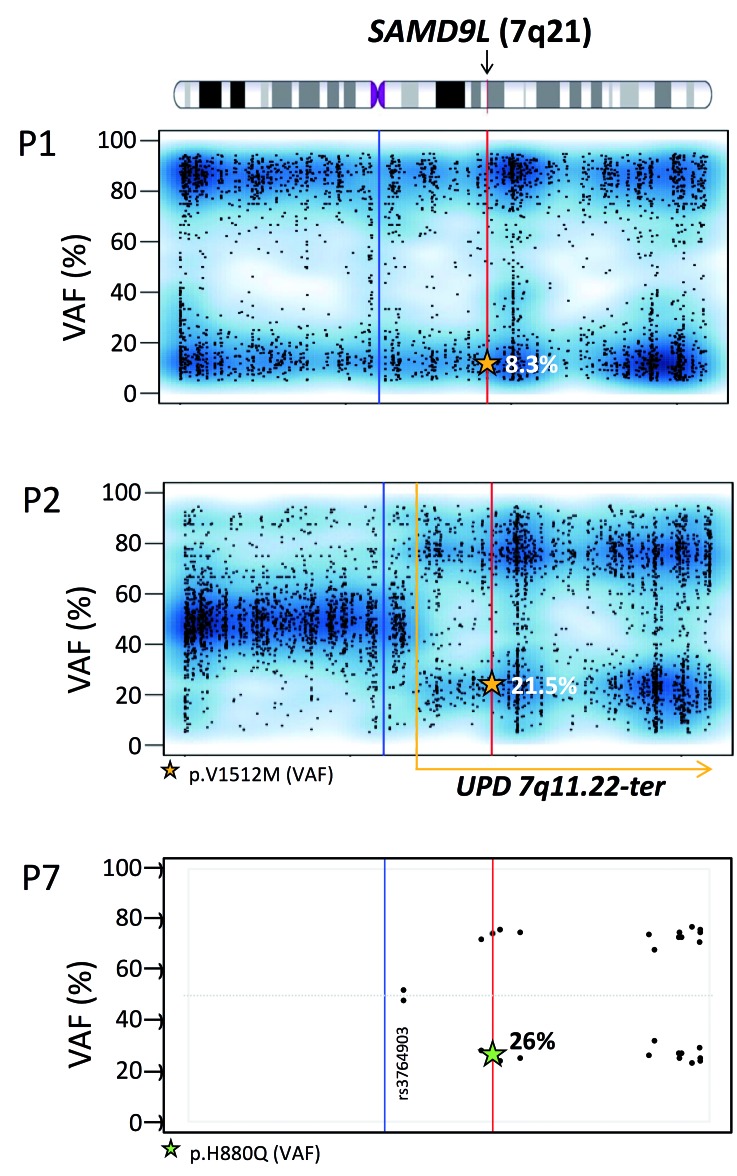
Figure 4.
Loss of mutated SAMD9L allele due to genomic deletion or mitotic recombination. Variant allelic frequency (VAF) scores for chromosome 7 in P1 and P2. single nucleotide polymorphisms and Indels detected using whole exome sequencing (~4000 variants with a VAF score >5% and <95%), show a complete loss of chromosome 7 in P1, as the VAF scores are either low or high. P2, unlike P1 demonstrates a partial loss of the chromosome 7 after position 7q11.22 towards the q terminal site. The read depth of the single nucleotide polymorphisms for P2 was maintained throughout for chromosome 7 with no loss thus confirming that loss of heterozygosity is due to UPD and not −7q. Whole exome sequencing VAF values are marked by a star within the graph. VAF: variant allelic frequency; UPD: uniparental isodisomy. Blue line: centromere; red line: SAMD9L gene position; yellow dotted line: start of UPD. For P7, targeted next-generation sequencing identified 14 informative (heterozygous) polymorphisms located on chromosome 7q with an average depth of 1036 reads (Online Supplementary Table S1). Single nucleotide polymorphisms are represented in a VAF graph depicting the skewing of heterozytosity towards one allelle occurring after position g.66098482 (rs3764903).