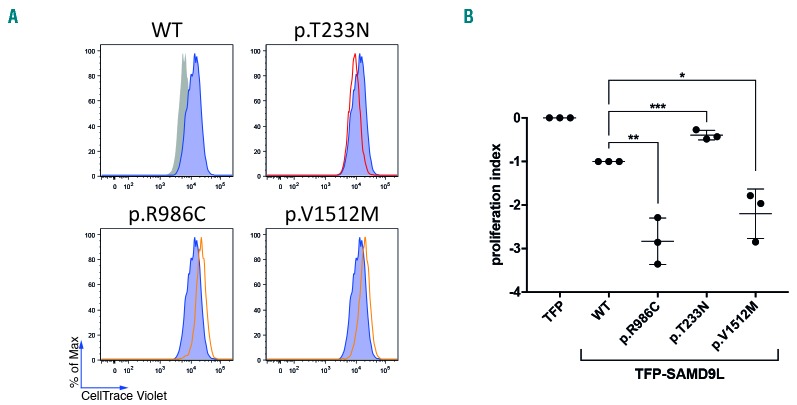
Figure 6.
Functional evaluation of SAMD9L mutations. (A,B) The effect of SAMD9L mutations on cell proliferation was assessed by dye dilution assays. 293FT cells were transiently transfected with TFP-SAMD9L wild type (WT), the disease-associated mutations p.R986C and p.V1512M, and the protective variant p.T233N previously reported by Tesi et al.20 (A) Histograms depict the dye levels in transfected cells. Dye levels were monitored in TFP-transfected cells (filled gray histograms) and compared to cells expressing uniformly intermediate levels of TFP-SAMD9L wild-type (blue histograms) or variants (red/orange lines), as indicated. A single representative experiment is shown. (B) Cumulative summary of three independent experiments on inhibition of cell proliferation associated with indicated TFP-SAMD9L mutations. Values (mean ± SD) are calculated based on a scale defined by 0 (dye levels in TFP-transfected cells) and −1 (dye levels in cells transfected with TFP-SAMD9L wild-type). Unpaired t-test, two tailed: *P<0.05; ** P<0.005; ***P<0.001.