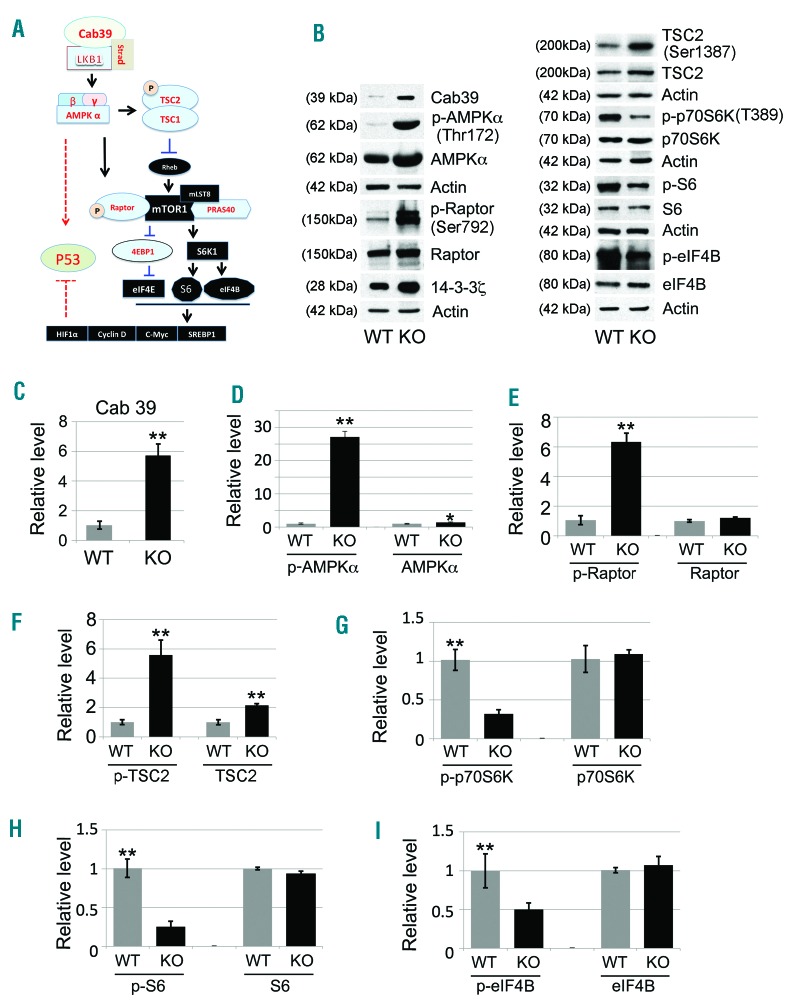
Figure 5.
Activation of the Cab39/AMPK/mTOR pathway in miR-144/451−/− erythroblasts. (A) Schematic illustration of the major signaling components in the Cab39/AMPK/mTOR molecular pathway. Cab39 expression leads to increased LKB1 activity in the Cab39/LKB1/STRAD protein complex, which activates its substrate AMPK. AMPK activation is vital for modulation of the mTOR signaling cascade and for potential stabilization of p53 activity, which subsequently governs the fate of the target cells, including their apoptosis, survival, and/or proliferation. (B) Western blot analysis of the expression of Cab39, p-AMPKα, p-Raptor, p-TSC2, p-p70S6K, p-S6, and p-eIF4B, along with their non-phosphorylated counterparts, in fetal liver (FL) erythroblasts grown in maturation medium for 24 hours, when all the cells were nucleated erythroblasts. 14-3-3ζ was used as a positive control, and actin was used as a sample loading control. Quantitative analyses of the protein intensity are shown in (C-I) as follows: (C) Cab39, (D) p-AMPKα/AMPKα, (E) p-Raptor/Raptor, (F) p-TSC2/TSC2, (G) p-p70S6K/p70S6K, (H) p-S6/S6, and (I) p-eIF4B/eIF4B. Signals were normalized to actin. Data are the mean values from 3 separate experiments. *P<0.05; **P<0.01 (t-test).