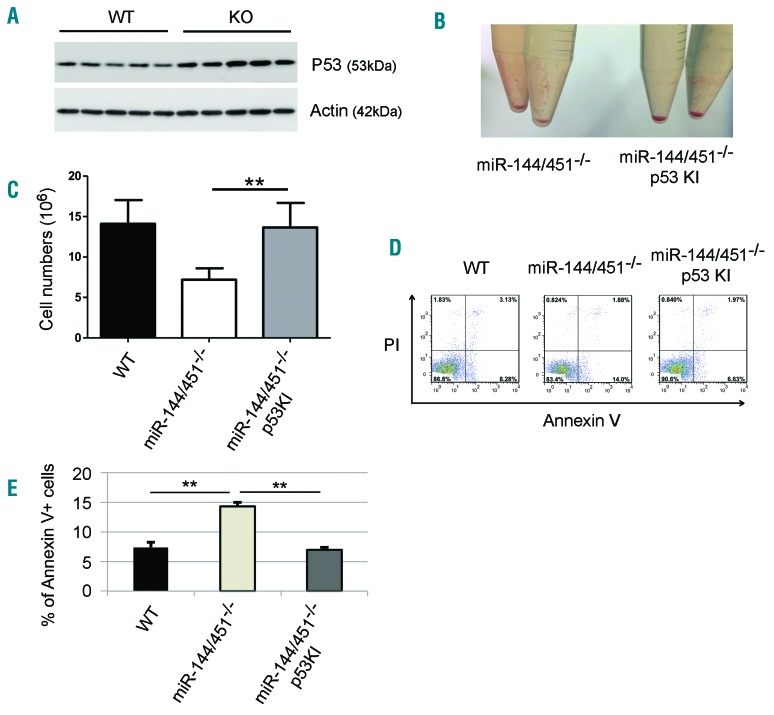
Figure 7.
The increased apoptosis of miR-144/451−/− erythroblasts is p53-dependent. (A) Western blot showing the protein levels of the tumor suppressor p53 in wild-type (WT) and miR-144/451−/− (KO) E14.5 fetal liver (FL) cells. Lineage negative-selected WT and KO E14.5 FL cells were grown in culture in erythroid maturation medium, and cells were harvested for Western blot analysis for p53 after 24 hours in culture. Actin was used as the loading control. (B) Gross view of the cell pellets from miR-144/451−/− and miR-144/451−/−/p53 knock-in (KI) double-mutant E14.5 FLs. (C) Total erythroblast number for whole E14.5 FLs from miR-144/451−/− and miR-144/451−/−/p53 KI double-mutant mice. miR-144/451−/− mice were crossed with p53-deficient KI mice.16,31 N=3 WT mice, n=6 KO mice, and n=6 double-mutant mice were used. **P<0.01 (t-test). (D) Flow cytometric analysis of apoptosis for miR-144/451−/− and miR-144/451−/−/p53 KI double-mutant E14.5 FL cells. WT FLs were used as controls. PI−Annexin V+ labeling was taken to indicate early apoptotic cells. (E) Quantitative analysis of flow cytometric data from (D).