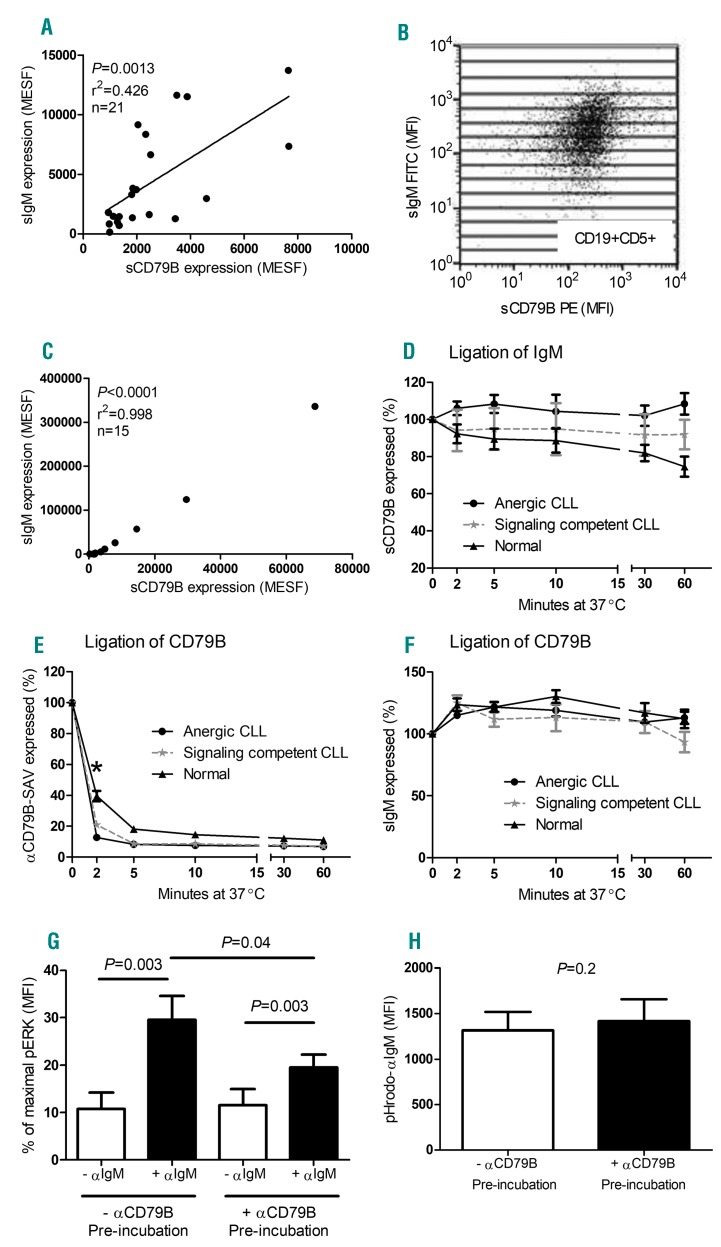
Figure 2.
Dissociation of BCR signaling and internalization in CLL cells. (A) A correlation was detected between the expression levels of surface (s)IgM and sCD79B on CD19+5+ cells derived from 21 CLL patients (both anergic and signaling competent B cells, Pearson’s correlation). Values are expressed as molecules of equivalent soluble fluorochrome (MESF) and derived from mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) values. (B) To examine the relationship within an individual patient, 15 subsets of CD19+5+ cells were created, as defined by increasing sIgM expression, and mean sCD79B MFI values were recorded within the same gate. (C) A representative patient demonstrating a correlation between sIgM and sCD79B. (D) The percentage of sCD79B receptor expression was measured on CLL and normal B cells following agonistic αIgM ligation; a gradual reduction and internalization of sCD79B on normal CD19+ B cells was detected after 60 min incubation (n=6; P=0.03*; Wilcoxon matched pairs test). In addition, CD79B internalization (E) and sIgM receptor expression (F) was measured upon αCD79B ligation, and compared between anergic, signaling competent and normal B cells. CD79B internalization occurred more rapidly (2 min time point) in anergic B cells compared to signaling competent and normal B cells (P=0.01 and P=0.001, respectively*; Mann-Whitney test), however, the percentage of sIgM receptor expression remained unchanged in all CLL cases. Finally, signaling competent CLL B cells were pre-incubated with agonistic αCD79B for 10mins at 37°C prior to αIgM stimulation to determine the effect of CD79B internalization on αIgM-induced pERK activation (G: n=9; pERK levels were normalized to the positive control), as well as pHrodo-αIgM uptake (H: n=9). Statistical analysis was performed via Wilcoxon matched pairs test. CLL: chronic lymphocytic leukemia; SAV: streptavidin-APC.