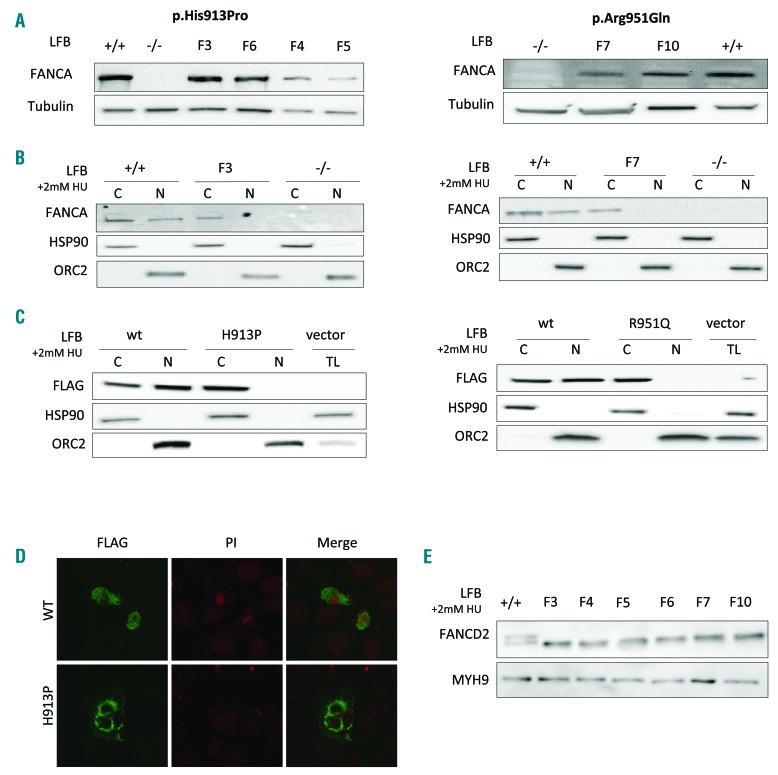
Figure 2.
Expression of p.His913Pro and p.Arg951Gln FANCA proteins. (A) Western blot of total lysates from lymphoblast (LFB) cells of patients carrying the p.His913Pro (F3, F4, F5 and F6) and the p.Arg951Gln (F7 and F10) mutations, showing that the mutant FANCA proteins are expressed. The controls are wild-type (+/+) LFB cells and LFB cells not expressing the FANCA protein (−/−) due to a homozygous large intragenic deletion (c.284-?_1826+?del) of FANCA. (B) Western blot of cytoplasmic (C) and nuclear (N) fractionated cellular lysates after 2 mM hydroxyurea treatment (24 hours) of LFB from patients F3 and F7, showing that the endogenous p.His913Pro and p.Arg951Gln proteins do not translocate to the nucleus. Controls +/+ and −/−, as indicated in (A). (C) Western blot of cytoplasmic (C), nuclear (N) fractionated, or total (TL) cellular lysates from 293T cells transfected with the wild-type (wt) or the mutant (H913P and R951Q) forms of FANCA tagged with FLAG, confirming the exogenous p.His913Pro and p.Arg951Gln FANCA proteins are retained in the cytoplasm. (D) Immunofluorescence analyses on 293T cells transfected as indicated in (C). Nuclei are stained with propidium iodide (PI). (E) Western blot of different LFB cells exposed to 2 mM hydroxyurea (24 hours) showing no monoubiquitination of the FANCD2 protein. Control +/+, as indicated in (A).