Fig. 6.
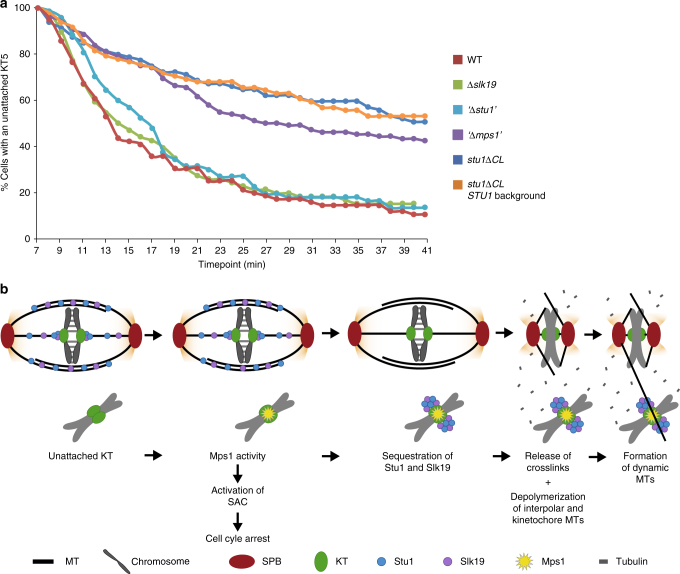
The enhanced formation of nrMTs facilitates the capturing of uaKTs. a Compromising the mitotic spindle by Stu1 removal is important for efficient capturing of uaKTs. Cells with the indicated genotypes (see Supplementary Table 1) were arrested in metaphase and uaKTs were produced as described in Fig. 2. Cells were observed in 1 min time intervals and the number of cells with an uaKT was determined. The number of cells with an uaKT observed 7 min after KT reactivation (see Supplementary Table 3) was set to 100%. The data shown is the result of one out of two independent experiments performed. Both had a very similar outcome. b Proposed model how sequestering of Stu1 and Slk19 enhances the formation of nrMTs, and thus promotes capturing of uaKTs. Mps1 localized at an uaKT induces the binding of Stu1 to this uaKT. This initiates the sequestering of Stu1 and Slk19 at the uaKT. Consequently, Stu1 and Slk19 are withdrawn from the spindle resulting in the depolymerization of kMTs and ipMTs. The free tubulin produced in this way then promotes the formation of dynamic nrMTs that scan the nucleus and facilitate the capturing of the uaKT