Fig. 8.
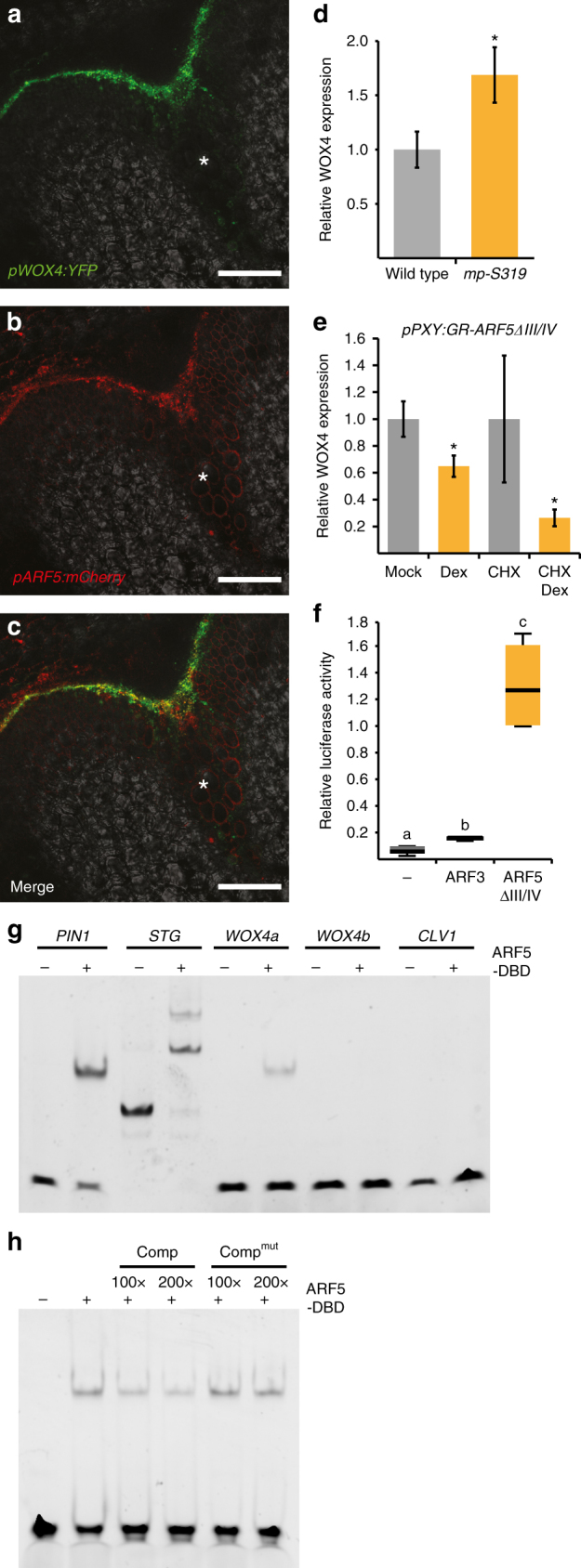
: ARF5 binds to the WOX4 promoter. a–c Confocal analysis of stem bases of plants carrying the pWOX4:YFP and the pARF5:mCherry reporter. Asterisks mark the vascular bundles. Size bars represent 100 µm. d, e Analysis of WOX4 transcript levels by quantitative RT-PCR at the stem base of wild-type and mp-S319 mutant pants (d) and in the second internode of pPXY:GR-ARF5∆III/IV plants after mock or Dex and CHX or CHX/Dex (e) treatments. Student’s T-test (wild type and mp-S319 p = 1.74E-02 and Mock and Dex p = 1.66E-02) or Welch’s T-test (CHX and CHX/Dex p = 1.29E-02) were performed comparing wild-type and mp-S319 mutants, mock and Dex and CHX and CHX/Dex, respectively (Sample sizes n = 3–6). Error bars represent ±standard deviation. Significance is indicated by the asterisk. f Analysis of relative luciferase activity of a pWOX4:LUC (firefly);p35S:LUC (Renilla) reporter in Arabidopsis protoplasts in the presence of p35S:ARF3, p35S:ARF5∆III/IV or no effector construct. Relative luciferase activity was determined by dual-luciferase assays. Statistical groups indicated by letters were determined by one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tamhane-T2 (CI 95%, Sample size n = 4–5). The T-bars that extend from the boxes (whiskers) are expected to include 95% of the data. g EMSAs probing DNA oligomers with proven (PIN1, STOMAGEN)50,53 or predicted (WOX4) binding capacities by the ARF5 DNA-binding domain (ARF5-DBD). An oligomer from the CLAVATA1 (CLV1) promoter was used as a negative control. Oligomer sequences are shown in Supplementary Table 1. h EMSAs probing the WOX4a oligomer in the presence of the non-labelled WOX4a competitor (comp) (in 100× and 200× excess) and in the presence of a mutated WOX4a oligomer (compmut) (with 100× and 200× excess)
