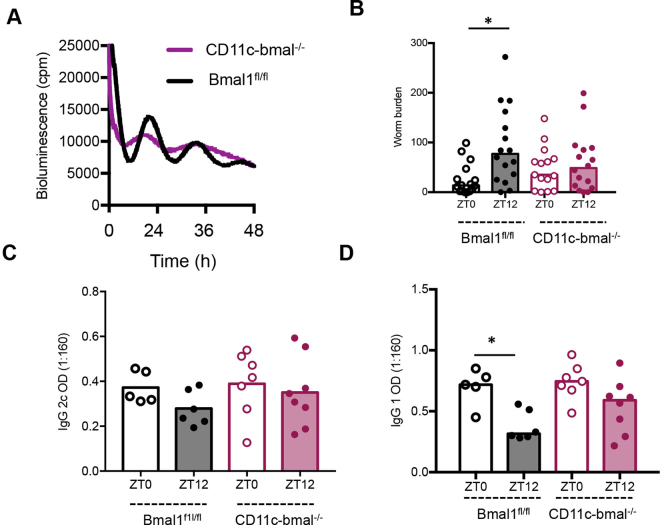
Figure 5.
Conditional deletion of bmal1 in dendritic cells abolishes diurnal variation in immune response to infection. Mice were generated which lacked bmal1 in CD11c positive cells (CD11c-bmal−/−). (A) Bone marrow derived dendritic cells cultured from CD11c-bmal−/− mice on a PER2::luc background and their wildtype counterparts (bmalfl/fl), were placed under photonmultiplier tubes (PMT) to monitor real-time luciferase activity as a readout of PER2 expression. (B) CD11c-bmal−/− and bmalfl/fl littermates were infected with T. muris at either ZT0 or ZT12. Worm burden (median presented) was assessed 21 days post infection, n = 15–16/group, combined data from two independent experiments. One way ANOVA, post hoc Tukey. (C,D) Parasite specific IgG2c and IgG1 production was measured on day 21. Serum was serially diluted and screened against parasite ES antigen (0.5 μg/ml); the data shown is dilution 1:160 only, as it falls within the linear range of the titration curve, n = 5–8, One Way ANOVA and post-hoc Tukey.