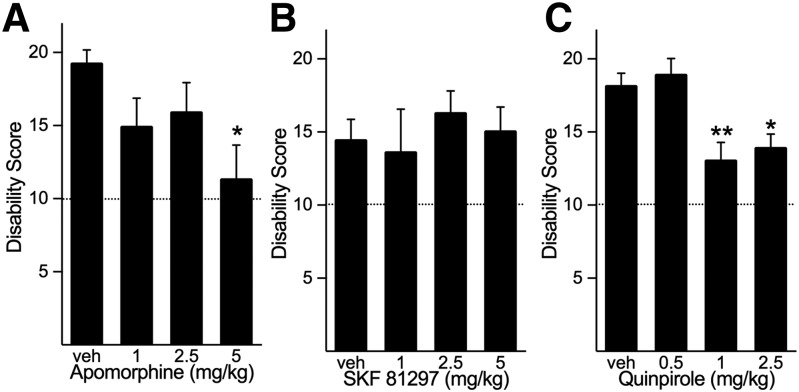
Fig. 2.
Effects of dopamine receptor agonists on dystonia induced by cerebellar microinjection of kainate. (A) The nonselective dopamine receptor agonist apomorphine dose-dependently reduced the severity of dystonia (one-way ANOVA; F3,29 = 3.259, P < 0.05, n = 8–10/dose). (B) The D1 dopamine receptor selective agonist SKF-81297 did not affect the severity of cerebellar kainic acid-induced dystonia (one-way ANOVA; F3,29 = 0.325, NS, n = 7–10/dose). (C) The D2 dopamine receptor selective agonist quinpirole significantly reduced the severity of dystonia (one-way ANOVA; F3,30 = 7.233, P < 0.001, n = 8 to 9/dose). Disability scores lower than 10 (dashed lines) suggest abnormal motor behavior, such as an unsteady gait, but not overt dystonia. Values represent the mean of the cumulative disability score in 1 hour ± S.E.M. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 compared with vehicle, Holm-Sidak multiple comparisons test.