Fig. 4.
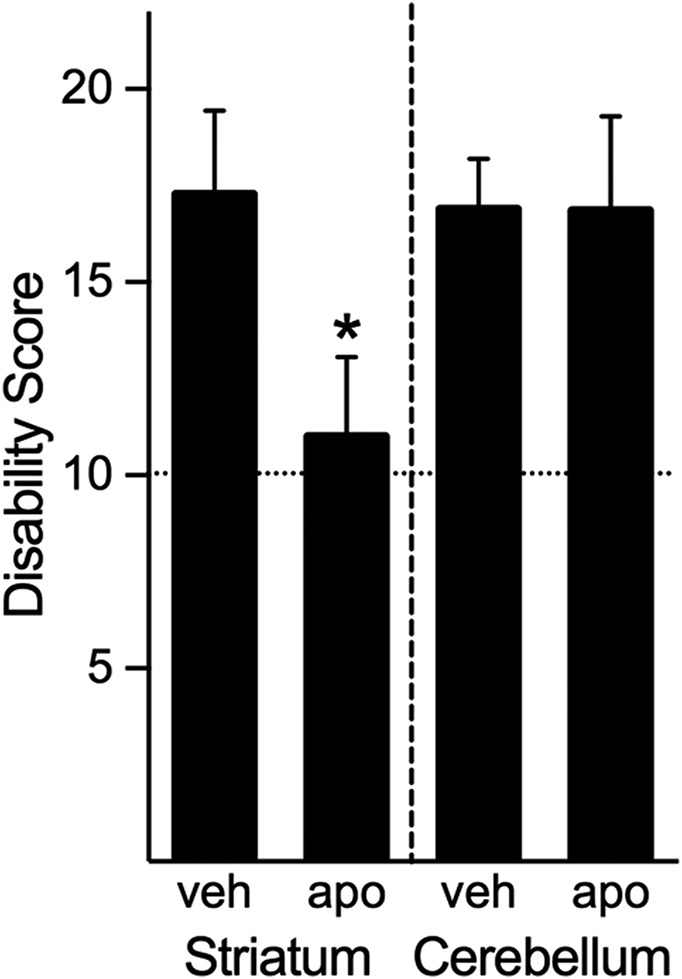
Regional analysis of the effects of apomorphine on dystonia induced by cerebellar microinjection of kainate. Microinjection of apomorphine into the striatum significantly reduced the severity of the dystonia (Student’s t test, one-tailed, P < 0.05 compared with saline), whereas cerebellar microinjection of apomorphine did not affect the severity of dystonia (Student’s t test, one-tailed, NS compared with saline). Disability scores lower than 10 (dashed lines) suggest abnormal motor behavior, such as an unsteady gait, but not overt dystonia. Values represent the mean of the cumulative disability score in 1 hour ± S.E.M.; *P < 0.05 compared with microinjection of vehicle in the same brain region.
