Figure 2.
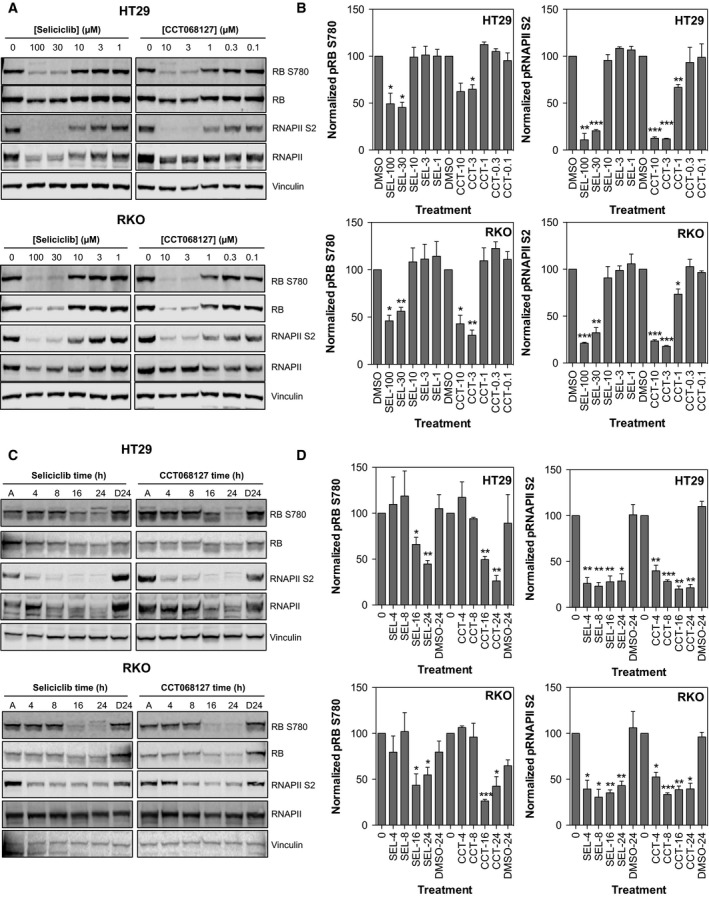
CCT068127 potently inhibits RB and RNA polymerase II phosphorylation in human cancer cells. (A) HT29 and RKO colon cancer cells were treated with increasing concentrations of CCT068127 or seliciclib for 24 h. Cell lysates were analyzed by western blotting for the phosphorylation of RB (a measure of CDK2 inhibition) and phosphorylation of RNA polymerase II (a measure of CDK9 inhibition). (B) Quantification of RB S780 and RNAPII S2 phosphorylation in (A), normalized to total RB or total RNAPII, respectively, and expressed as a percentage of the DMSO control (mean percentage of control values presented from three independent repeats ± SE, significant difference from control indicated by *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, two‐tailed t‐test). (C) HT29 and RKO cells were treated with equiactive (3xGI 50, SRB assay) concentrations of CCT068127 (2.55 μm for HT29 and 1.98 μm for RKO) or seliciclib (45 μm for HT29 and 30 μm for RKO) for the indicated times. A: asynchronously growing, untreated cells; D24: cells treated with DMSO for 24 h. Cell lysates were analyzed by western blotting for the indicated proteins. (D) Quantification of RB S780 and RNAPII S2 phosphorylation in (C), normalized to total RB or total RNAPII, respectively, and expressed as a percentage of the time 0 control (mean percentage of control values presented from three independent repeats ± SE, significant difference from control indicated by *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, two‐tailed t‐test).
