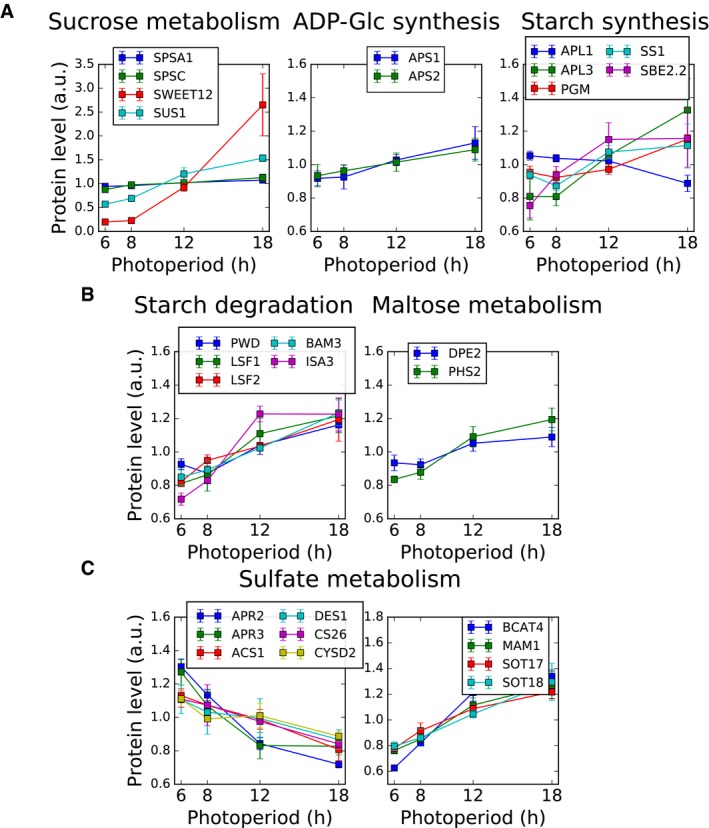
Significantly changing proteins involved in the partitioning of sugars to sucrose and starch during the day, including sucrose metabolism (sucrose‐phosphate synthase, SPSA1, SPSC; bidirectional sugar transporter SWEET12; sucrose synthase, SUS1), ADP‐Glc synthesis (glucose‐1‐phosphate adenylyltransferase small subunits, APS1, APS2) and starch synthesis (glucose‐1‐phosphate adenylyltransferase large subunits, APL1, APL3; phosphoglucomutase, PGM; starch synthase, SS1; 1,4‐alpha‐glucan‐branching enzyme, SBE2.2).
Significantly up‐regulated proteins involved in metabolism of starch during the night, including starch degradation (phosphoglucan, water dikinase, PWD; phosphoglucan phosphatase, LSF1, LSF2; beta‐amylase, BAM3; iso‐amylase, ISA3) and maltose metabolism (4‐alpha‐glucanotransferase, DPE2; alpha‐glucan phosphorylase, PHS2).
Significantly down‐regulated proteins in sulphate metabolism. Includes 5′‐adenylylsulphate reductases (APR2, APR3), cysteine synthases (ACS1, DES1, CS26, CYSD2), methionine aminotransferase (BCAT4), methylthioalkylmalate synthase (MAM1) and cytosolic sulphotransferases (SOT17, SOT18).
= 3).