Figure EV4. Chk1 inhibition induces an E2F7/8‐dependent cell cycle arrest and reduces cell survival.
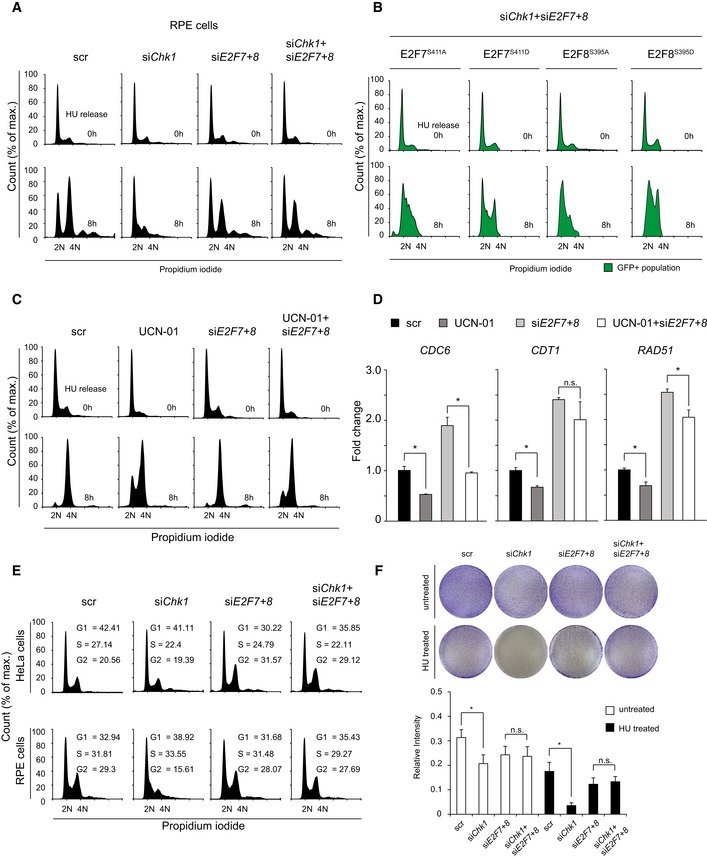
- FACS cell cycle profiles at 0 and 8 h after HU release from propidium iodide‐stained RPE cells incubated with siRNAs directed against Chk1 and E2F7/8. Scrambled (scr) siRNA was used as control.
- FACS cell cycle profiles at 0 and 8 h after HU release from propidium iodide‐stained GFP‐positive HeLa/TO cells transfected with siRNA against Chk1 and E2F7/8. Doxycycline was added to the cells 16 h before HU release.
- FACS cell cycle profiles from propidium iodide‐stained HeLa cells treated with UCN‐01. HeLa cells were first transfected with scramble or siE2F7+8, then exposed to HU and the Chk1 inhibitor UCN‐01 for 16 h, and eventually harvested at 0 and 8 h after HU release.
- Transcript levels of E2F7/8 target genes after 16 h of HU treatment, measured by qPCR. Fold changes were adjusted to the scrambled condition.
- Cell cycle distribution of HeLa and RPE cells transfected with siRNA against Chk1 and E2F7/8 under unperturbed condition. Scrambled (scr) siRNA was used as control.
- Clonogenic survival assay of HeLa cells transfection with siRNA against Chk1 and E2F7/8 under un‐treated or HU‐treated condition. Cells were transfected with indicated siRNA for 24 h and reseeded at a low density and grow for 4 days. Scrambled (scr) siRNA was used as control. Histogram shows the quantification of relative intensity from each condition (n = 2 independent experiments).
