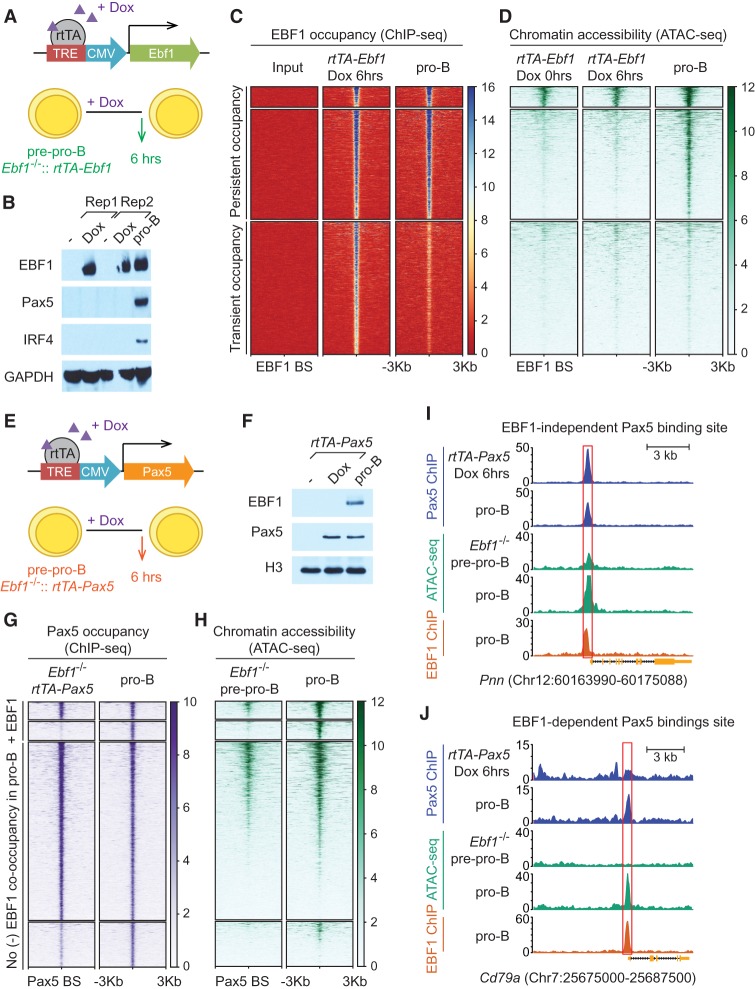
Figure 5.
EBF1-induced chromatin accessibility is required for Pax5 occupancy at a set of B-lineage-specific genes. (A) Scheme of a “Tet-on”-based doxycycline-inducible EBF1 expression construct, rtTA-Ebf1. Ebf1−/− pre-pro-B cells were transduced with rtTA-Ebf1 retrovirus. Cells were treated with doxycycline (Dox) for 6 h to induce EBF1 expression. (rtTA) Tetracycline-controlled transactivator rtTA-advanced; (TRE) tetracycline response element. (B) Immunoblot analysis of cell lysates from Ebf1−/−::rtTA-Ebf1 pre-pro-B cells at 0 or 6 h after 1 µg/mL doxycycline treatment and from CD19-positive pro-B cells to detect the expression of EBF1, Pax5, and IRF4. (Rep) Replicate. (C,D) ChIP-seq analysis (C) and ATAC-seq analysis (D) to detect EBF1 occupancy and chromatin accessibility before (0 h) and after (6 h) doxycycline treatment. EBF1 peaks and ATAC signals are centered around ±3 kb of EBF1-bound sites and grouped into three clusters according to the persistence or transience of EBF1 occupancy and pre-existing or de novo accessibility. (E) Scheme of a “Tet-on”-based doxycycline-inducible Pax5 construct (rtTA-Pax5). (F) Immunoblot analysis to detect the expression of EBF1 and Pax5 in cell lysates from Ebf1−/−::rtTA-Pax5 pre-pro-B cells at 0 or 6 h after doxycycline treatment and from pro-B cells. (G) Pax5 occupancy in Ebf1−/−::rtTA-Pax5 pre-pro-B cells (6 h after doxycycline treatment) and in pro-B cells centered on Pax5-bound sites identified in pro-B cells. The top two clusters are co-occupied by EBF1 in EBF1-expressing pro-B cells. The bottom two clusters lack EBF1 co-occupancy in pro-B cells. (H) Chromatin accessibility in Ebf1−/− pre-pro-B cells and pro-B cells centered on Pax5-bound sites identified in the pro-B-cell sample. Pax5 peaks and ATAC signals are grouped into four clusters according to the presence or absence of EBF1 co-occupancy in pro-B cells and according to Pax5 occupancy in Ebf1−/− pre-pro-B cells and EBF1-expressing pro-B cells. (I,J) Pax5 occupancy in Ebf1−/−:rtTA-Pax5 pre-pro-B cells (6 h after doxycycline treatment) and in pro-B cells, chromatin accessibility in Ebf1−/− pre-pro-B cells and pro-B cells, and EBF1 occupancy in pro-B cells at the EBF1-independent Pax5 target Pnn locus (I) and EBF1-dependent Pax5 target Cd79a locus (J).