Figure 1.
Differentiation and Development of hiPSC Line-Induced Human Dopaminergic Neurons and Astrocytes
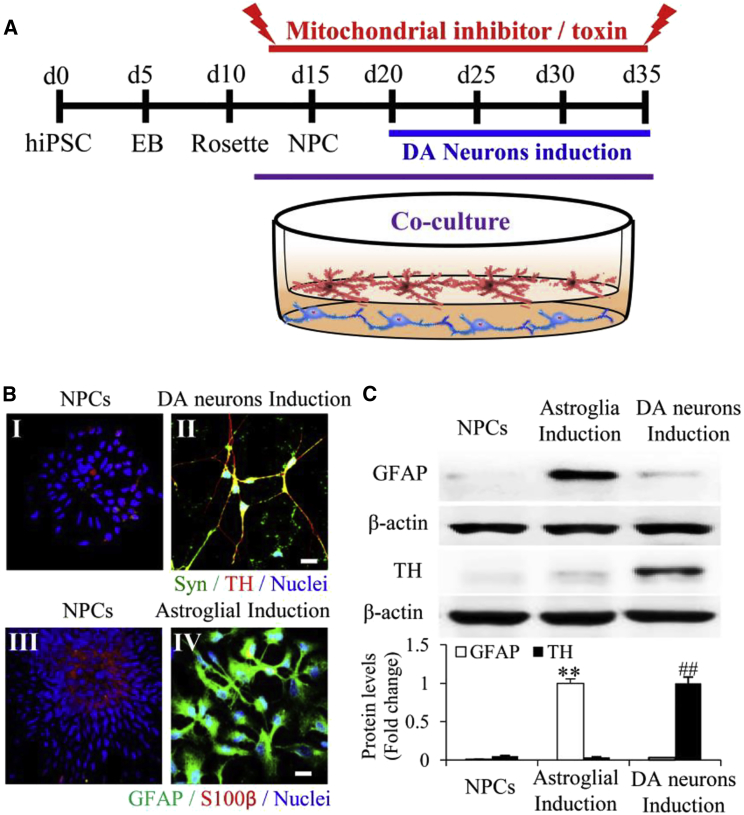
(A) A schematic representation of the differentiation of mitochondrial inhibitor/toxin (KCN or rotenone)-treated hiPSC line-induced DA neurons with astroglial co-culture. EB, embryoid body.
(B) Immunocytochemistry of synaptophysin (Syn)-positive (green) puncta and TH (red) in neural progenitor cells (NPCs; I) and mature DA neurons (II) and mature astroglial marker (GFAP, green) and astroglial progenitor marker (S100β, red) in NPCs (III) and astrocytes induced for 9 months (IV).
(C) Representative immunoblots for GFAP and TH expression in NPCs, astrocytes induced for 9 months, and DA neurons. β-actin was used as a protein loading control. ∗∗p < 0.01 versus NPCs and DA neurons (open bars, GFAP), and ##p < 0.01 versus NPCs and DA neurons (black bars, TH).
Scale bars, 25 μm in (B). For (C), statistical analysis was performed using StatView software (SAS Institute, v.5.0.1). One-way ANOVA was used for repeated-measure analysis, followed by Fisher's protected least significant difference for post hoc comparisons. Data are presented as means ± SEM. n = 3 independent experiments.