Figure 7.
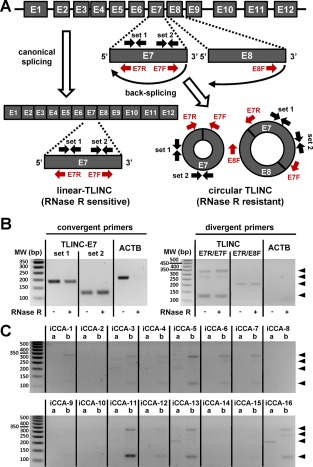
Experimental evidence of TLINC circular isoforms. (A) Schematic representation of TLINC RNA processing into linear RNA (canonical splicing) or circular RNA (back‐splicing). Several sets of convergent and divergent PCR primers were designed to detect specific linear and circular isoforms. (B) RNA was extracted from Huh28 cells after 16 hours of treatment with 1 ng/mL TGFβ. RNase R treatment was performed prior to RT‐PCR analysis. Convergent primers (left panel) detected specific TLINC‐E7 transcripts in both RNase R untreated and treated samples. For ACTB (a housekeeping gene highly expressed), no amplification was observed after RNase R treatment. By using a specific set of divergent primers located on exons E7 and E8, several TLINC circular isoforms were highlighted (black arrowheads). (C) RNAs were extracted from 16 human iCCA tumors. RT‐PCR analysis was performed using a specific set of divergent primers located on exons E7 and E8, as indicated at the top of the panels (a, E7R/E8F; b, E7R/E7F). Black arrowheads highlight TLINC circular isoforms. Abbreviations: bp, base pair; MW, molecular weight.
