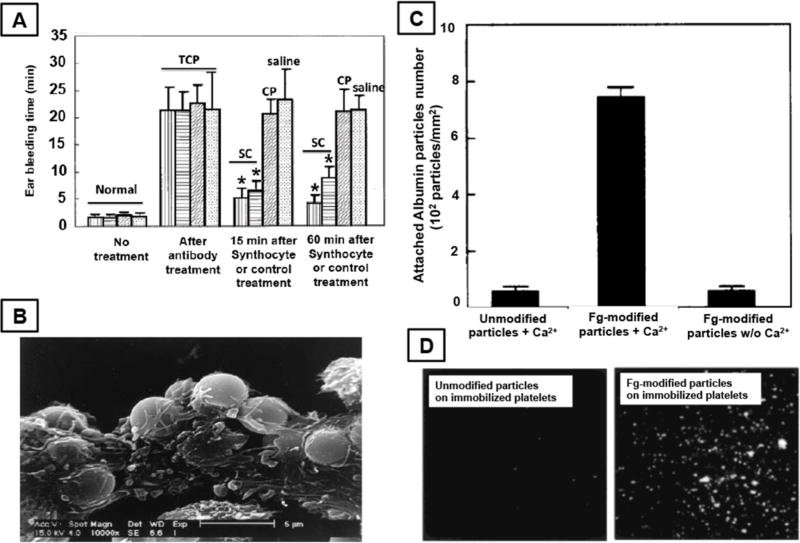
Figure 12.
Selected results from studies carried out with various fibrinogen-coated particle designs. 12A shows the effect of administering fibrinogen-coated albumin microcapsules (Synthocyte™) in reducing ear punch bleeding time in thrombocytopenic rabbits, where induction of thrombocytopenia (TCP) significantly increased bleeding time from normal levels and administration of Synthocyte™ particles (SC) could significantly reduce bleeding time in these animals, compared to administration of control particles (CP) or saline; 12B shows scanning electron micrograph of the Synthocyte™ particles incorporated with platelets and fibrin in hemostatic clots; 12C shows the ability of fibrinogen-coated albumin particles to bind to platelet-immobilized surfaces in absence versus presence of Ca++ ions, compared to binding of unmodified albumin particles and 12D shows representative fluorescence microscopy images of these binding studies, confirming high binding of fibrinogen-coated particles and establishing that these particles can interact with active platelets under flow environment, possibly via interaction with platelet surface integrin GPIIb-IIIa, thereby mimicking and amplifying the active platelet aggregation component of hemostasis. Figure components adapted and reproduced with permission.[419,420] Copyright 1999, Macmillan Publishers Ltd and 2001, American Chemical Society.