Extended Data Figure 1. Multiple models have been proposed to explain the cell of origin for BE.
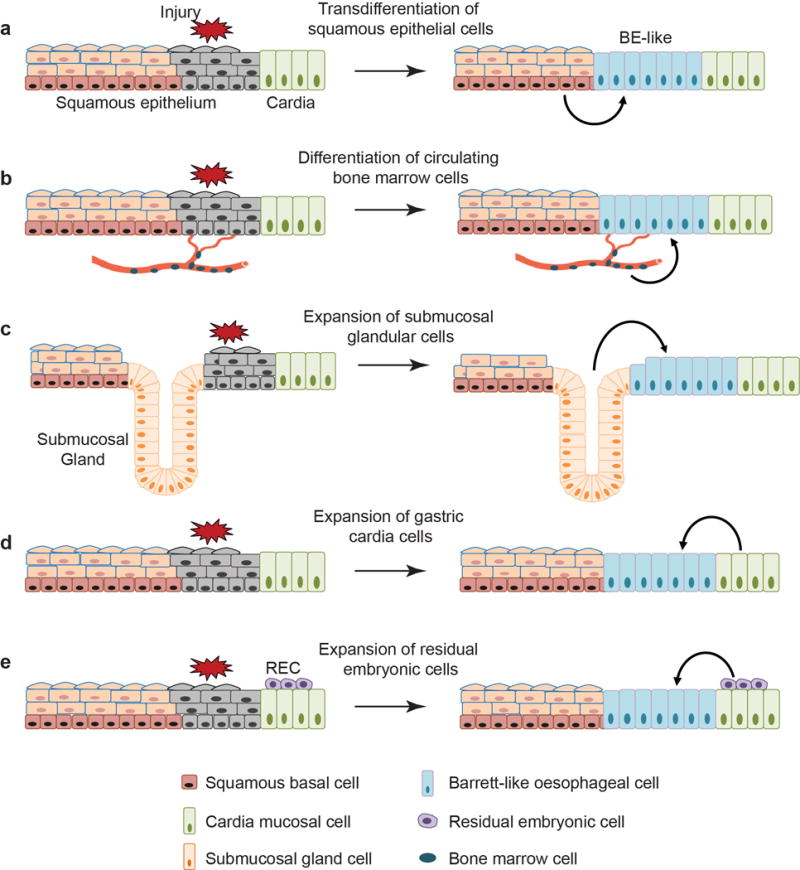
a, Transdifferentiation of the stratified squamous oesophageal epithelium into Barrett’s epithelium. b, Transdifferentiation of circulating bone marrow cells into Barrett’s epithelium. c, Expansion of the oesophageal submucosal gland leads to BE. d, Stem/progenitor cells (Lgr5+) in the cardia mucosa differentiate into BE. e, Expansion of the quiescent residual embryonic cells (RECs) at the SCJ leads to BE formation. Note that none of the studies recapitulates the pathological changes characteristically associated with BE in humans, e.g. presence of intestinal goblet cells.
