Extended Data Figure 4. The transitional columnar epithelium is present at the SCJ of normal mice.
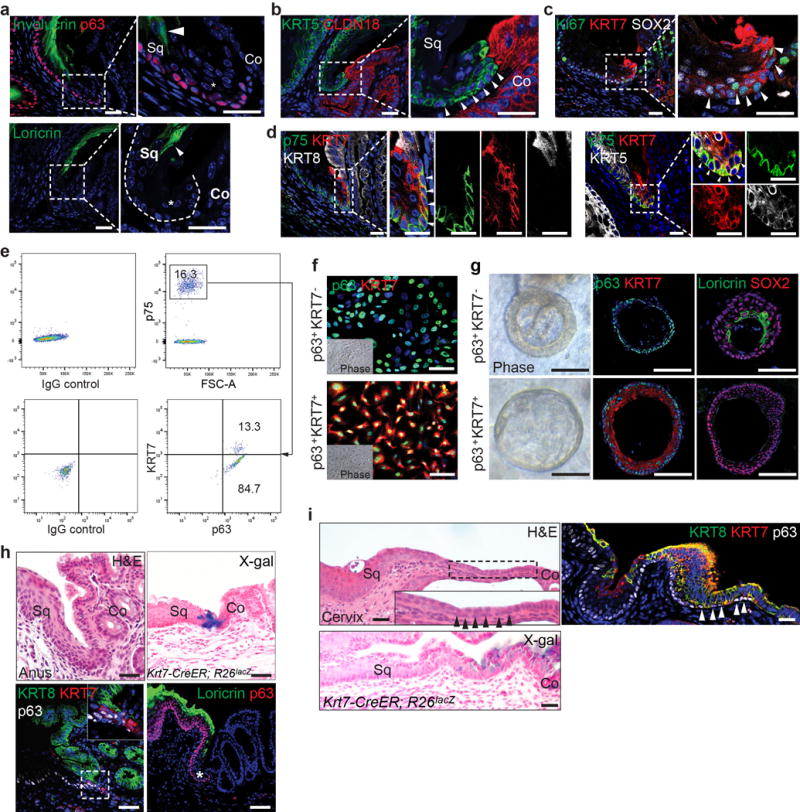
a, The transitional epithelium (star) does not express Involucrin and Loricrin, markers labeling the stratified squamous epithelium. n=11. b, Basal cells of the transitional epithelium express KRT5 but not the cardia epithelial marker CLDN18. n=11. c, The KRT7+ transitional basal cells are highly proliferative (Ki67+, arrowheads). n=3. d, The transitional basal cells of at the SCJ express p75, KRT7 and KRT5, but not KRT8. Note that p75 and KRT5 are also expressed in the neighboring squamous basal cells. n=5. e, FACS analysis reveals p75+ basal cells include two subpopulations, squamous basal cells (p63+ KRT7−) and transitional basal cells (p63+ KRT7+). n=3 independent experiments. f, A representative culture of p63+KRT7− and p63+KRT7+ basal progenitor cells. Note that p63+ KRT7+ transitional basal cells in the colony are loose unlike the cobblestone characteristic of squamous basal cell colony (p63+ KRT7−). n=5 per group. g, p63+KRT7− and p63+KRT7+ basal progenitor cells generate keratinized (Loricrin+, KRT7−) and non-keratinized (Loricrin−, KRT7+) epithelium in organoid, respectively. n=5 per group. h, i, The transitional epithelium is also present at the SCJ of the anus (h) and cervix (i). Lineage trancing with the Krt7-CreER mouse line confirmed KRT7+ cells serve as progenitors for the transitional epithelium. n=3 per group. Abbreviation: Sq, stratified squamous epithelium; Co, columnar epithelium. Scale bar, 20 μm.
