FIG. 2.
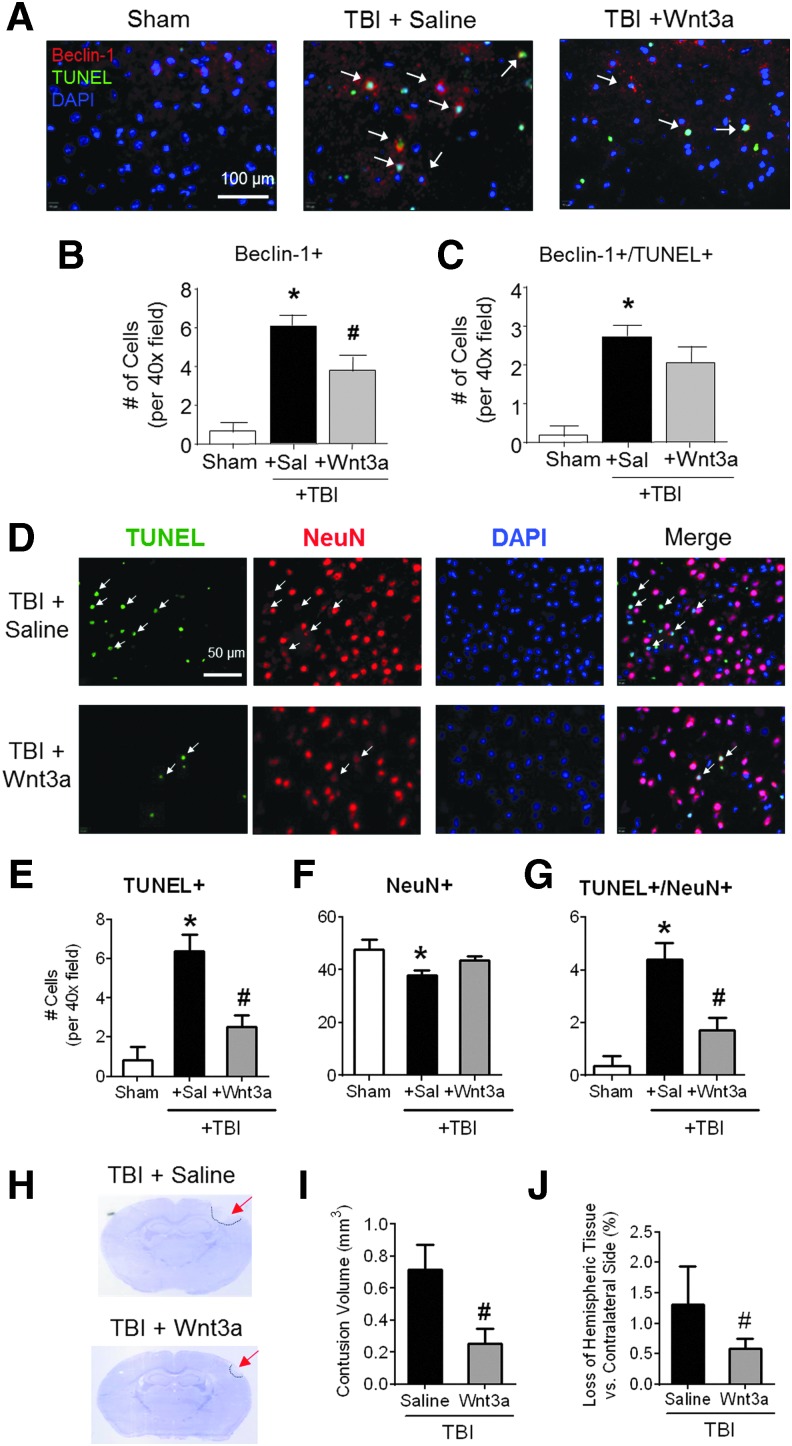
Neuroprotective effects of Wnt3a against autophagic cell death and brain damage following mild traumatic brain injury (TBI) (A–C) The presence of autophagic cell death was visualized by immunohistochemistry at 2 days post-TBI. (A) Representative images of immunofluorescence (red: Beclin-1, green: TUNEL, blue: DAPI). (B) Quantification of Beclin-1+ cells per 40 × field. (C) Quantification of Beclin-1+/TUNEL+ co-labeled cells per 40 × field. *p < 0.05, compared with Sham. #p < 0.05, compared with TBI+Saline. A total of 600–700 images were quantified. n = 4 for Sham group, n = 7 for both TBI+Saline and TBI+Wnt3a groups. (D) Representative immunofluorescence images are shown (green: TUNEL, red: NeuN, blue: DAPI) revealed significantly greater levels of TUNEL+ cells, as well as TUNEL+/NeuN+ co-labeled cells (arrows). (E) Quantification of total number of TUNEL+ cells. (F) Quantification of total number of NeuN+ cells. (G) Quantification of total number of TUNEL+/NeuN+ colocalized cells. *p < 0.05, compared with Sham. #p < 0.05, compared with TBI+Saline. A total of 500–600 images were quantified. n = 5 per group. (H) Representative images of Nissl-stained sections for post-TBI animals receiving either intranasal vehicle saline injection or Wnt3a injection at 1 h post-injury and 1 day post-injury. Tissue loss can be observed in the ipslateral hemisphere (bordered by dashed line). (I) Volumetric analysis by the Cavalieri method was used to calculate total injury volumes from cumulative summation of injury areas of adjacent sections spanning the length of the contusion. (J) Hemispheric tissue loss was calculated by comparing the difference in volume between the ipsilateral hemisphere and the contralateral hemisphere. *p < 0.05, compared with Sham. #p < 0.05, compared with TBI+Saline. n = 5 per group. Color image is available online at www.liebertpub.com/neu