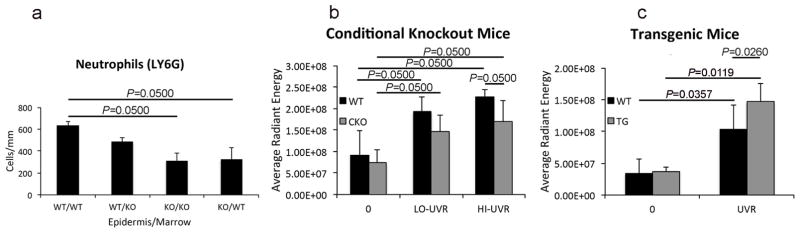
Figure 1. Slug controls UVR-induced neutrophil influx into the skin.
(a) UVR induced significantly greater neutrophil influx in mice with WT epidermis and WT bone marrow (WT/WT) than in mice with KO epidermis and WT (KO/WT) or KO marrow (KO/KO). Data shown as means of four to six mice±SD (one-way ANOVA and Dunnett’s multiple comparison statistic). (b,c) Signal from a fluorescent neutrophil elastase probe was similar in unexposed CKO and TG mice and WT littermates. There was significant induction of neutrophil elastase activity by UVR; however, UVR-exposed CKO mice had significantly reduced and TG mice had significantly increased signal compared to UVR-exposed WT mice. Data shown as means of three to six adult mice per group ±SD (pairwise comparison with one-way Mann-Whitney statistic).