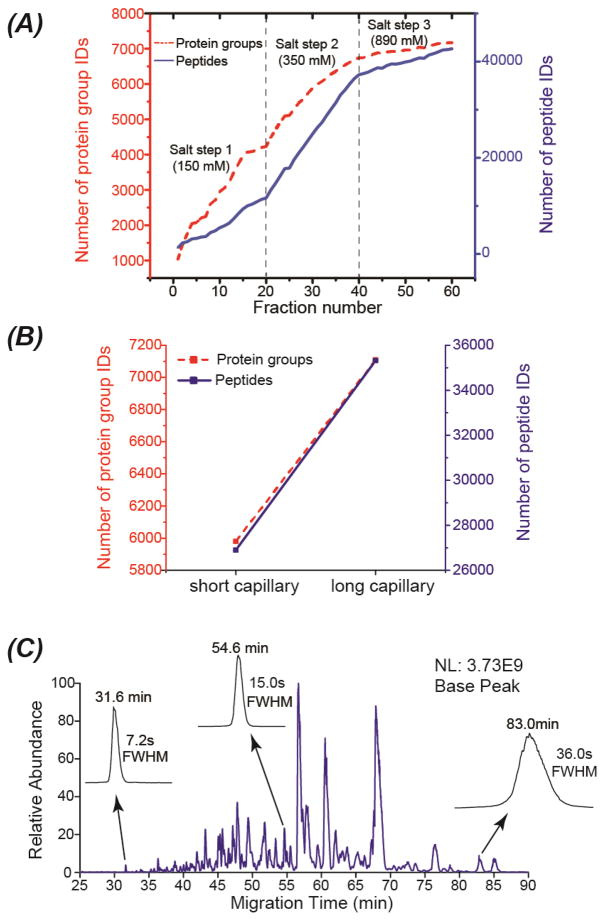
Fig. 2.
Summary of the results from the mouse brain proteome digest using SCX-RPLC-CZE-MS/MS. Three salt steps were employed for step-wise elution of peptides from the SCX to the RPLC. (A) The accumulated numbers of protein group and unique peptide IDs vs. the number of fractions. A 71-cm separation capillary was used for CZE-MS/MS. (B) Comparison of the number of protein group and unique peptide IDs from the twenty LC fractions corresponding to the second salt step analyzed by the CZE-MS/MS with a 71-cm separation capillary (short) or a 92-cm separation capillary (long). (C) An electropherogram of one SCX-RPLC fraction analyzed by CZE-MS/MS with the 92-cm separation capillary. The migration time and the full width at half maximum (FWHM) of three peptides were shown in the figure.