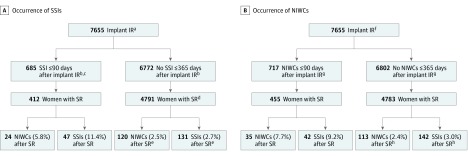
Figure 2. Incidence of Surgical Site Infection (SSI) and Noninfectious Wound Complications (NIWCs) After Secondary Reconstruction (SR) Stratified by SSI and NIWC After Immediate Implant Reconstruction .
aSSIs attributable to the immediate implant reconstruction (implant IR) were identified within 90 days of the index procedure. Follow-up to identify SR was performed through 365 days after mastectomy.
bIndicates attributable to implant IR.
cOf these, 273 (39.9%) did not have a secondary reconstructive procedure within 365 days of the index surgery.
dExcludes 9 women with an SSI or cellulitis within 30 days before SR, not attributable to implant IR.
eIf we included the 105 women with SSI more than 90 days after implant IR who had SR in the uninfected category, an additional 8 women had an SSI and 6 women had an NIWC after SR, bringing the total number of SSIs attributable to SR to 139 (2.9%) and the total number of NIWCs attributable to SR to 126 (2.6%). Compared with the incidence of SSI and NIWCs for women who had SSI within 90 days after implant IR, the differences remain statistically significant (P < .001).
fNIWCs attributable to the immediate implant reconstruction were identified within 90 days of the index procedure. Follow-up to identify SR was performed through 365 days after mastectomy.
gIndicates attributable to implant IR.
hIf we included the 79 women with NIWCs more than 90 days after implant IR who had SR into the uncomplicated category, an additional 2 women had an SSI and 3 women had an NIWC after SR, bringing the total number of SSIs attributable to SR to 144 (3.0%) and the total number of NIWCs attributable to SR to 116 (2.4%). Compared with the incidence of SSI and NIWCs for women who had NIWCs within 90 days after implant IR, the differences remain statistically significant (P < .001).