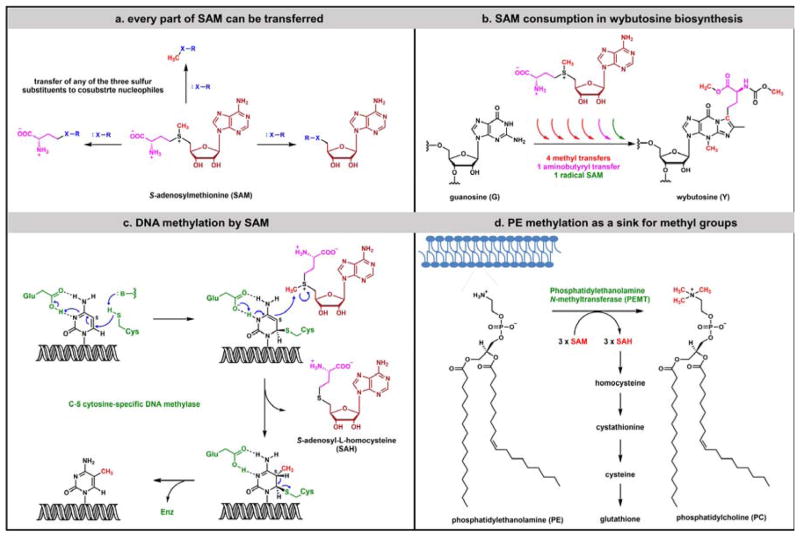
Figure 12.
S-adenosyl methionine (SAM) as thermodynamically activated alkyl transfer metabolite: (a) the sulfonium group in SAM activates all three substituents for transfer as electrophilic alkyl fragments, although methyl group transfer is by far the most common; (b) the versatility of SAM is evident in formation of the wybutosine modified base in tRNA. Six equivalents of SAM are consumed, four are moved as [CH3+] equivalents, the fifth as a [CH3•] equivalent. The sixth molecule of SAM instead donates an electrophilic aminobutyryl group; (c) DNA methylation at C5 of Cytidine residues occurs by the indicated addition/elimination mechanism with SAM as the one carbon donor; (d) SAM is also involved in membrane phospholipid maturation, converting hundreds of thousands to millions of phosphatidylethanolamine to phosphatidylcholine molecules via three consecutive N-methyl transfers in mammalian cells.